变量的作用
存数据 被程序调用和操作
标记数据
声明变量
name = “Ydh” 变量名 = 变量值
变量定义规范:
变量名只能是 字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
一下关键字不能声明为变量名【python的语法关键词、python内置变量】
变量命名习惯
1、驼峰体(每个首字母大写)
AgeOfOldboy = 56
NumberOfStudents = 80
2、下划线(官方推荐)
age_of_oldboy = 56
number_of_students = 80
定义变量的Low方式
变量名为中文、拼音
变量名过长
变量名不达意
如:
你的年龄 = 20 age_of_oldboy = 20
ni_denianling = 20
the_ni_de_mingzi = 20 your_name = 20
name1 = 1
name2 = "北京"
调用变量
print(age_of_oldboy)
修改变量值
age_of_oldboy = 30
常量
永远不变的量 例如π=3.14.....
python里边没有一个专门的语法代表常亮,程序员约定:常量变量名全部为大写
如:AGE_OF_OLDBOY = 20
读取用户输入
input()
name = input("input name:")
注释
作用:
1、注释掉不用的代码
2、描述代码段的意思
代码注释原则:
1、不用全部加注释
2、只需要在自己觉得重要或不好理解的部分加注释即可
3、注释可以用中文或英文,但绝对不要用拼音
基本类型
数字
整数int
长整型long
浮点型float
负数
字符集
文本str
字节bytes
布尔
True/Flase
数据集
列表list
元组tuple
字典dict
有序字典
无序字典
集合set
有序集合
无序集合
int(整型)
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-23~231-1
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-263~263-1
long(长整型)
python的长整数没有指定位宽。即python没有限制长整数数值的大小,但实际上由于机器的内存有限,我们使用的长整数数值不可能无限大。
浮点数float
简单的理解就是小数
字符串
在python中,加了引号的字符都被认为是字符串(包括单引号、双引号、三引号)
单双引号没有任何区别,只有下面的情况下,需要考虑单双引号的配合
msg = "I'm 20 years old!"
多引号作用是多行字符串必须用多引号
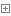
msg = ‘’‘ 我爱北京天安门 天安门上太阳升 ’‘’ print(msg)
字符串拼接
字符串可以相加和相乘,字符串只能和字符串进行拼接
name + age
name * 10 把name的值打印10次
布尔类型
真/假 True/False
用于逻辑判断,是正确的为True,还是错误的为False!
计算机为什么要描述这种条件呢?
因为可以根据条件结果来做不通的事情,如:

if a > b :
print ("this is a bigger number than b")
else:
print("this is a smaller number than b")
格式化输出
%s 代表 字符串
%d代表 数字
%f代表 浮点数 float
运算符
算数运算
“+ - * / 、取余数:% 、幂:** x的y次幂、取整数//”

比较运算
"等于:== 、不等于:!= 、不等于:<>、> 、<、>= 、<="

逻辑运算
"与and、或or、非not"

赋值运算
“等于=、加等于+=、减等于-=、乘等于*=、除等于/=、取模等于%=、幂等于**=、取整除等于//=”

成员运算

身份运算

位运算

单分支
if条件:
满足条件后要执行的代码
双分支
if条件: 满足条件后要执行的代码 else: if条件不满足就走这里的代码
多分支
if条件: 满足条件后要执行的代码 elif: 如果上边的条件不满足就走这个 elif: 如果上边的条件不满足就走这个 elif: 如果上边的条件不满足就走这个
语法:
while 条件: 条件成立,执行代码...
pass #就是什么都不做
死循环dead loop
count = 0
while True:
print ("count:", count)
count += 1
break 用于完全结束一个循环,跳出循环体 执行后面的语句
continue 跳出本次循环,进行下次循环
练习:猜年龄游戏
练习一、输入姓名、性别,判断如果是女生,打印我喜欢女生,否则,打印一起来搞基!

name = input("input name:")
sex = input("input sex:")
if sex == "女" :
print("我喜欢女生!")
else:
print("一起来搞基!")
'''
测试结果1:
input name:join
input sex:男
一起来搞基!
-----------
测试结果2:
input name:小薇
input sex:女
我喜欢女生!
'''
练习二、输入姓名、性别、年龄,判断如果是女生且年龄小于28岁,打印我喜欢女生,否则,打印姐弟恋也很好!

name = input("input name:")
sex = input("input sex:")
age = int(input("input age:"))
if sex == "女" :
if age < 28:
print("我喜欢女生")
else:
print("姐弟恋也很好!")
'''
测试结果1:
input name:小薇
input sex:女
input age:25
我喜欢女生
----------------
测试结果2:
input name:小薇
input sex:女
input age:29
姐弟恋也很好!
测试结果3:
input name:john
input sex:男
input age:25
输出为空
练习三、输入姓名、性别、年龄,判断如果是女生且年龄小于28岁,打印我喜欢女生,否则,打印姐弟恋也很好!如果是男生,打印一起来搞基!
name = input("input name:")
sex = input("input sex:")
age = int(input("input age:"))
if sex == "女" :
if age < 28:
print("我喜欢女生")
else:
print("姐弟恋也很好!")
elif sex == "男":
print("一起来搞基!")
else:
print("sex 输入不正确!")
1、流程控制;
匹配成绩的小程序,成绩有ABCDE 5个等级,与分数的对应关系如下:
A 90-100
B 80-89
C 60-79
D 40-59
E 0-39

while True:
score = float(input("input your score:"))
if score >100 or score < 0 :
print("没有这个成绩")
elif score >= 90:
print("A")
elif score >= 80 and score <=89:
print("B")
elif score >= 60 and score <= 79:
print("C")
elif score >= 40 and score <=59:
print("D")
elif score >= 0 and score <=39:
print("E")
2、猜年龄练习
练习一
优化猜年龄游戏,允许用户最多猜3次,中间猜对了,直接跳出循环

name = 25
count = 1
while True:
user_input = int(input("猜年龄,请输入年龄:"))
if count > 3:
break
elif user_input == name:
print("恭喜猜对了!")
break
count += 1
练习二
优化猜年龄游戏,允许用户最多猜3次,猜了3次后,再问是否还继续玩,
如果用户选y,就再允许3次,依次循环,如果用户输入n ,就退出程序

name = 25
count = 1
while True:
if count > 3:
while True:
judge = input("是否要继续玩游戏,y/n:")
if judge == "y":
count = 0
break
elif judge == "n":
print("谢谢光临!")
exit()
else:
print("输入不正确!")
else:
user_input = int(input("猜年龄,请输入年龄:"))
if user_input == name :
print("恭喜猜对了!")
break
elif user_input < 25:
print("think bigger!!")
elif user_input > 25:
print("think smaller!!")
count += 1
3、while循环练习
练习一、循环1-100 个数

count = 1
while count <= 100:
print("loop:",count)
count += 1
练习二、循环1-100 里边的偶数:

count = 1
while count <= 100:
if count%2==0: #偶数能够整除2 ,相反就是基数
print("loop:",count)
count += 1
练习三、循环打印1-100,第50次不打印值,第60-80次,打印对应值的平方

count = 1
while count <= 100:
if count == 50:
pass
if count >=60 and count <=80:
print("loop count 的平方是:",count * count)
else:
print("loop:",count)
count += 1
练习四、循环终止语句

count = 1
while count <= 100:
print("loop:",count)
if count == 5:
break
count += 1
while 条件匹配:
条件匹配成功,执行此处代码
else:
条件不匹配,执行此处代码
例子:
count = 1
while count <= 5: #当count<=5的时候,条件匹配,执行下边的代码
print("loop:",count)
count += 1
else:
print("循环终止了!") #当count=6的时候不匹配while条件,执行此处代码
输出:
loop: 1
loop: 2
loop: 3
loop: 4
loop: 5
循环终止了!
本章作业:
基础需求:
让用户输入用户名密码
认证成功后显示欢迎信息
输错三次后退出程序
升级需求:
可以支持多个用户登录(提示:通过列表存多个账户信息)
用户3次认证失败后,退出程序,
再次启动程序尝试登录时,还是锁定状态(提示:需把用户锁定的状态存到文件里)
如对本文有疑问, 点击进行留言回复!!


python中逻辑与或(and、or)和按位与或异或(&、|、^)区别

基于Python编写一个计算器程序,实现简单的加减乘除和取余二元运算

网友评论