木兰围场坝上影视基地,芙蓉王妃好看吗,3D字谜彩酷酷caikuku
a*作为最常用的路径搜索算法,值得我们去深刻的研究。路径规划项目。先看一下维基百科给的算法解释:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/a*_search_algorithm
a *是最佳优先搜索它通过在解决方案的所有可能路径(目标)中搜索导致成本最小(行进距离最短,时间最短等)的问题来解决问题。 ),并且在这些路径中,它首先考虑那些似乎最快速地引导到解决方案的路径。它是根据加权图制定的:从图的特定节点开始,它构造从该节点开始的路径树,一次一步地扩展路径,直到其一个路径在预定目标节点处结束。
在其主循环的每次迭代中,a *需要确定将其部分路径中的哪些扩展为一个或多个更长的路径。它是基于成本(总重量)的估计仍然到达目标节点。具体而言,a *选择最小化的路径
f(n)= g(n)+ h(n)
其中n是路径上的最后一个节点,g(n)是从起始节点到n的路径的开销,h(n)是一个启发式,用于估计从n到目标的最便宜路径的开销。启发式是特定于问题的。为了找到实际最短路径的算法,启发函数必须是可接受的,这意味着它永远不会高估实际成本到达最近的目标节点。
维基百科给出的伪代码:
function a*(start, goal)
// the set of nodes already evaluated
closedset := {}
// the set of currently discovered nodes that are not evaluated yet.
// initially, only the start node is known.
openset := {start}
// for each node, which node it can most efficiently be reached from.
// if a node can be reached from many nodes, camefrom will eventually contain the
// most efficient previous step.
camefrom := an empty map
// for each node, the cost of getting from the start node to that node.
gscore := map with default value of infinity
// the cost of going from start to start is zero.
gscore[start] := 0
// for each node, the total cost of getting from the start node to the goal
// by passing by that node. that value is partly known, partly heuristic.
fscore := map with default value of infinity
// for the first node, that value is completely heuristic.
fscore[start] := heuristic_cost_estimate(start, goal)
while openset is not empty
current := the node in openset having the lowest fscore[] value
if current = goal
return reconstruct_path(camefrom, current)
openset.remove(current)
closedset.add(current)
for each neighbor of current
if neighbor in closedset
continue // ignore the neighbor which is already evaluated.
if neighbor not in openset // discover a new node
openset.add(neighbor)
// the distance from start to a neighbor
//the "dist_between" function may vary as per the solution requirements.
tentative_gscore := gscore[current] + dist_between(current, neighbor)
if tentative_gscore >= gscore[neighbor]
continue // this is not a better path.
// this path is the best until now. record it!
camefrom[neighbor] := current
gscore[neighbor] := tentative_gscore
fscore[neighbor] := gscore[neighbor] + heuristic_cost_estimate(neighbor, goal)
return failure
function reconstruct_path(camefrom, current)
total_path := {current}
while current in camefrom.keys:
current := camefrom[current]
total_path.append(current)
return total_path
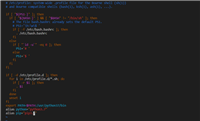
下面是udacity课程中路径规划项目,结合上面的伪代码,用python 实现a*
import math
def shortest_path(m,start,goal):
sx=m.intersections[start][0]
sy=m.intersections[start][1]
gx=m.intersections[goal][0]
gy=m.intersections[goal][1]
h=math.sqrt((sx-gx)*(sx-gx)+(sy-gy)*(sy-gy))
closedset=set()
openset=set()
openset.add(start)
gscore={}
gscore[start]=0
fscore={}
fscore[start]=h
camefrom={}
sumg=0
new=0
bool=false
while len(openset)!=0:
max=1000
for new in openset:
print("new",new)
if fscore[new]<max:
max=fscore[new]
#print("max=",max)
new=new
current=new
print("current=",current)
if current==goal:
return reconstruct_path(camefrom,current)
openset.remove(current)
closedset.add(current)
#dafult=m.roads(current)
for neighbor in m.roads[current]:
bool=false
print("key=",neighbor)
a={neighbor}
if len(a&closedset)>0:
continue
print("key is not in closeset")
if len(a&openset)==0:
openset.add(neighbor)
else:
bool=true
x= m.intersections[current][0]
y= m.intersections[current][1]
x1=m.intersections[neighbor][0]
y1=m.intersections[neighbor][1]
g=math.sqrt((x-x1)*(x-x1)+(y-y1)*(y-y1))
h=math.sqrt((x1-gx)*(x1-gx)+(y1-gy)*(y1-gy))
new_gscore=gscore[current]+g
if bool==true:
if new_gscore>=gscore[neighbor]:
continue
print("new_gscore",new_gscore)
camefrom[neighbor]=current
gscore[neighbor]=new_gscore
fscore[neighbor] = new_gscore+h
print("fscore",neighbor,"is",new_gscore+h)
print("fscore=",new_gscore+h)
print("__________++--------------++_________")
def reconstruct_path(camefrom,current):
print("已到达lllll")
total_path=[]
total_path.append(current)
for key,value in camefrom.items():
print("key",key,":","value",value)
while current in camefrom.keys():
current=camefrom[current]
total_path.append(current)
total_path=list(reversed(total_path))
return total_path
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持移动技术网。
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复

Python 实现将numpy中的nan和inf,nan替换成对应的均值
python爬虫把url链接编码成gbk2312格式过程解析

网友评论