荡女基卡,张逸凡陆梦馨,dingxing
本文实例讲述了python简单读写xls格式文档的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
1. 模块安装
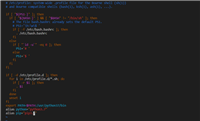
使用pip install命令安装,
即:
pip install xlrd
pip install xlwt
如下图:
2. python 代码
import xlrd
import xlwt
import datetime
def set_style(name,height,format,bold=false):
style = xlwt.xfstyle()
if format.strip()!='':
style.num_format_str =format
font = xlwt.font()
font.name=name
font.bold=bold
font.color_index=4
font.height=height
alignment = xlwt.alignment()
#horz_general, horz_left, horz_center, horz_right, horz_filled, horz_justified, horz_center_across_sel, horz_distributed
alignment.horz = xlwt.alignment.horz_center
#vert_top, vert_center, vert_bottom, vert_justified, vert_distributed
alignment.vert = xlwt.alignment.vert_center
style.alignment = alignment
style.font=font
return style
def set_colstyle(sheet,cindex):
col=sheet.col(cindex)
col.width =256*20
#col.height =100
def writexls(path):
wb = xlwt.workbook()
sheet = wb.add_sheet('测试',cell_overwrite_ok=true)
set_colstyle(sheet,3)
#标题
heads=['姓名','学科','分数','日期']
for h in range(0,len(heads)):
sheet.write(0,h,heads[h],set_style('arial',300,'',true))
#数据
sheet.write_merge(1,2,0,0,'张三',set_style('arial',300,'',false))
sheet.write(1,1,'语文',set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(1,2,85,set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(1,3,datetime.date.today(),set_style('arial',240,'yyyy/mm/dd',false))
sheet.write(2,1,'数学',set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(2,2,85,set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(2,3,datetime.date.today(),set_style('arial',240,'yyyy/mm/dd',false))
sheet.write_merge(3,4,0,0,'李四',set_style('arial',300,'',false))
sheet.write(3,1,'语文',set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(3,2,95,set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(3,3,datetime.date.today(),set_style('arial',240,'yyyy/mm/dd',false))
sheet.write(4,1,'数学',set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(4,2,95,set_style('arial',240,'',false))
sheet.write(4,3,datetime.date.today(),set_style('arial',240,'yyyy/mm/dd',false))
wb.save(path)
def ismerge(sheet,merge,r,c):
#merge=sheet.merged_cells
for m in merge:
if r>=m[0] and r<m[1] and c==m[2]:
r=m[0]
c==m[2]
break
return r,c
def readxls(path):
wb=xlrd.open_workbook(path,formatting_info=true)
#sheetname=wb.sheet_names()[0]
sheet=wb.sheet_by_index(0)
rows=sheet.nrows
cols=sheet.ncols
merge=sheet.merged_cells
#merged_cells返回的这四个参数的含义是:(row,row_range,col,col_range),
#其中[row,row_range)包括row,不包括row_range
print('--------------------------------------------------------------------')
for r in range(0,rows):
liststr = []
for c in range(0,cols):
merg=ismerge(sheet,merge,r,c)
if (sheet.cell(merg[0],merg[1]).ctype==3):
data_value=xlrd.xldate_as_tuple(sheet.cell_value(merg[0],merg[1]),wb.datemode)
#print(datetime.date(*data_value[:3]).strftime('%y/%m/%d'))
liststr.append(datetime.date(*data_value[:3]).strftime('%y/%m/%d'))
else:
#print(sheet.cell_value(merg[0],merg[1]))
liststr.append(sheet.cell_value(merg[0],merg[1]))
#print(sheet.cell(merg[0],merg[1]).value)
#print(sheet.cell(r,c).ctype)
print(' |\t'.join(str(s) for s in liststr if s not in [none]))
print('--------------------------------------------------------------------')
if __name__ == '__main__':
#writexls('h:\测试.xls')
readxls('h:\测试.xls')
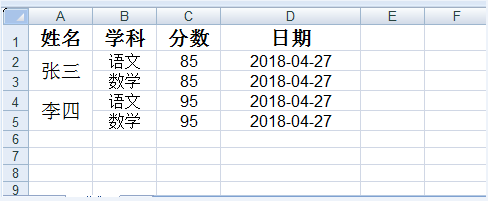
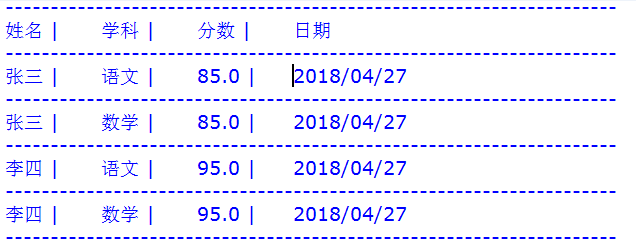
3.效果展示
更多关于python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《python操作excel表格技巧总结》、《python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》、《python文本文件操作技巧汇总》、《python数据结构与算法教程》、《python函数使用技巧总结》、《python字符串操作技巧汇总》及《python入门与进阶经典教程》
希望本文所述对大家python程序设计有所帮助。
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复

Python 实现将numpy中的nan和inf,nan替换成对应的均值
python爬虫把url链接编码成gbk2312格式过程解析

网友评论