小白 张艾亚,u5i格机,中央美院分数线
属于混合编程的问题。较全面的介绍一下,不仅限于题主提出的问题。
以下讨论中,python指它的标准实现,即cpython(虽然不是很严格)
本文分4个部分
1. c/c++ 调用 python (基础篇)— 仅讨论python官方提供的实现方式
2. python 调用 c/c++ (基础篇)— 仅讨论python官方提供的实现方式
3. c/c++ 调用 python (高级篇)— 使用 cython
4. python 调用 c/c++ (高级篇)— 使用 swig
练习本文中的例子,需要搭建python扩展开发环境。具体细节见[搭建python扩展开发环境 - 蛇之魅惑 - 知乎专栏](http://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/python-dev/20150730)
**1 c/c++ 调用 python(基础篇)**
python 本身就是一个c库。你所看到的可执行体python只不过是个stub。真正的python实体在动态链接库里实现,在windows平台上,这个文件位于 %systemroot%\system32\python27.dll。
你也可以在自己的程序中调用python,看起来非常容易:
```
//my_python.c
#include <python.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
py_setprogramname(argv[0]);
py_initialize();
pyrun_simplestring("print 'hello python!'\n");
py_finalize();
return 0;
}
```
在windows平台下,打开visual studio命令提示符,编译命令为
```
cl my_python.c -ic:\python27\include c:\python27\libs\python27.lib
```
在linux下编译命令为
```
gcc my_python.c -o my_python -i/usr/include/python2.7/ -lpython2.7
```
在mac os x 下的编译命令同上
产生可执行文件后,直接运行,结果为输出
```
hello python!
```
python库函数pyrun_simplestring可以执行字符串形式的python代码。
虽然非常简单,但这段代码除了能用c语言动态生成一些python代码之外,并没有什么用处。我们需要的是c语言的数据结构能够和python交互。
下面举个例子,比如说,有一天我们用python写了一个功能特别强大的函数:
```
def great_function(a):
return a + 1
```
接下来要把它包装成c语言的函数。我们期待的c语言的对应函数应该是这样的:
```
int great_function_from_python(int a) {
int res;
// some magic
return res;
}
```
首先,复用python模块得做‘import’,这里也不例外。所以我们把great_function放到一个module里,比如说,这个module名字叫 great_module.py
接下来就要用c来调用python了,完整的代码如下:
```
#include <python.h>
int great_function_from_python(int a) {
int res;
pyobject *pmodule,*pfunc;
pyobject *pargs, *pvalue;
/* import */
pmodule = pyimport_import(pystring_fromstring("great_module"));
/* great_module.great_function */
pfunc = pyobject_getattrstring(pmodule, "great_function");
/* build args */
pargs = pytuple_new(1);
pytuple_setitem(pargs,0, pyint_fromlong(a));
/* call */
pvalue = pyobject_callobject(pfunc, pargs);
res = pyint_aslong(pvalue);
return res;
}
```
从上述代码可以窥见python内部运行的方式:
* 所有python元素,module、function、tuple、string等等,实际上都是pyobject。c语言里操纵它们,一律使用pyobject *。
* python的类型与c语言类型可以相互转换。python类型xxx转换为c语言类型yyy要使用pyxxx_asyyy函数;c类型yyy转换为python类型xxx要使用pyxxx_fromyyy函数。
* 也可以创建python类型的变量,使用pyxxx_new可以创建类型为xxx的变量。
* 若a是tuple,则a[i] = b对应于 pytuple_setitem(a,i,b),有理由相信还有一个函数pytuple_getitem完成取得某一项的值。
* 不仅python语言很优雅,python的库函数api也非常优雅。
现在我们得到了一个c语言的函数了,可以写一个main测试它
```
#include <python.h>
int great_function_from_python(int a);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
py_initialize();
printf("%d",great_function_from_python(2));
py_finalize();
}
```
编译的方式就用本节开头使用的方法。
在linux/mac osx运行此示例之前,可能先需要设置环境变量:
bash:
```
export pythonpath=.:$pythonpath
```
csh:
```
setenv pythonpath .:$pythonpath
```
**2 python 调用 c/c++(基础篇)**
这种做法称为python扩展。
比如说,我们有一个功能强大的c函数:
```
int great_function(int a) {
return a + 1;
}
```
期望在python里这样使用:
```
>>> from great_module import great_function
>>> great_function(2)
3
```
考虑最简单的情况。我们把功能强大的函数放入c文件 great_module.c 中。
```
#include <python.h>
int great_function(int a) {
return a + 1;
}
static pyobject * _great_function(pyobject *self, pyobject *args)
{
int _a;
int res;
if (!pyarg_parsetuple(args, "i", &_a))
return null;
res = great_function(_a);
return pylong_fromlong(res);
}
static pymethoddef greatemodulemethods[] = {
{
"great_function",
_great_function,
meth_varargs,
""
},
{null, null, 0, null}
};
pymodinit_func initgreat_module(void) {
(void) py_initmodule("great_module", greatemodulemethods);
}
```
除了功能强大的函数great_function外,这个文件中还有以下部分:
* 包裹函数_great_function。它负责将python的参数转化为c的参数(pyarg_parsetuple),调用实际的great_function,并处理great_function的返回值,最终返回给python环境。
* 导出表greatemodulemethods。它负责告诉python这个模块里有哪些函数可以被python调用。导出表的名字可以随便起,每一项有4个参数:第一个参数是提供给python环境的函数名称,第二个参数是_great_function,即包裹函数。第三个参数的含义是参数变长,第四个参数是一个说明性的字符串。导出表总是以{null, null, 0, null}结束。
* 导出函数initgreat_module。这个的名字不是任取的,是你的module名称添加前缀init。导出函数中将模块名称与导出表进行连接。
在windows下面,在visual studio命令提示符下编译这个文件的命令是
```
cl /ld great_module.c /o great_module.pyd -ic:\python27\include c:\python27\libs\python27.lib
```
/ld 即生成动态链接库。编译成功后在当前目录可以得到 great_module.pyd(实际上是dll)。这个pyd可以在python环境下直接当作module使用。
在linux下面,则用gcc编译:
```
gcc -fpic -shared great_module.c -o great_module.so -i/usr/include/python2.7/ -lpython2.7
```
在当前目录下得到great_module.so,同理可以在python中直接使用。
**本部分参考资料**
* 《python源码剖析-深度探索动态语言核心技术》是系统介绍cpython实现以及运行原理的优秀教程。
* python 官方文档的这一章详细介绍了c/c++与python的双向互动[extending and embedding the python interpreter](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3a//docs.python.org/2/extending/%23extending-index)
* 关于编译环境,本文所述方法仅为出示原理所用。规范的方式如下:[3\. building c and c++ extensions with distutils](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3a//docs.python.org/2/extending/building.html%23building)
* 作为字典使用的官方参考文档 [python/c api reference manual](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3a//docs.python.org/2/c-api/%23c-api-index)
用以上的方法实现c/c++与python的混合编程,需要对python的内部实现有相当的了解。接下来介绍当前较为成熟的技术cython和swig。
**3 c/c++ 调用 python(使用cython)**
在前面的小节中谈到,python的数据类型和c的数据类型貌似是有某种“一一对应”的关系的,此外,由于python(确切的说是cpython)本身是由c语言实现的,故python数据类型之间的函数运算也必然与c语言有对应关系。那么,有没有可能“自动”的做替换,把python代码直接变成c代码呢?答案是肯定的,这就是cython主要解决的问题。
安装cython非常简单。python 2.7.9以上的版本已经自带easy_install:
```
easy_install -u cython
```
在windows环境下依然需要visual studio,由于安装的过程需要编译cython的源代码,故上述命令需要在visual studio命令提示符下完成。一会儿使用cython的时候,也需要在visual studio命令提示符下进行操作,这一点和第一部分的要求是一样的。
继续以例子说明:
```
#great_module.pyx
cdef public great_function(a,index):
return a[index]
```
这其中有非python关键字cdef和public。这些关键字属于cython。由于我们需要在c语言中使用“编译好的python代码”,所以得让great_function从外面变得可见,方法就是以“public”修饰。而cdef类似于python的def,只有使用cdef才可以使用cython的关键字public。
这个函数中其他的部分与正常的python代码是一样的。
接下来编译 great_module.pyx
```
cython great_module.pyx
```
得到great_module.h和great_module.c。打开great_module.h可以找到这样一句声明:
```
__pyx_extern_c dl_import(pyobject) *great_function(pyobject *, pyobject *)
```
写一个main使用great_function。注意great_function并不规定a是何种类型,它的功能只是提取a的第index的成员而已,故使用great_function的时候,a可以传入python string,也可以传入tuple之类的其他可迭代类型。仍然使用之前提到的类型转换函数pyxxx_fromyyy和pyxxx_asyyy。
```
//main.c
#include <python.h>
#include "great_module.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
pyobject *tuple;
py_initialize();
initgreat_module();
printf("%s\n",pystring_asstring(
great_function(
pystring_fromstring("hello"),
pyint_fromlong(1)
)
));
tuple = py_buildvalue("(iis)", 1, 2, "three");
printf("%d\n",pyint_aslong(
great_function(
tuple,
pyint_fromlong(1)
)
));
printf("%s\n",pystring_asstring(
great_function(
tuple,
pyint_fromlong(2)
)
));
py_finalize();
}
```
编译命令和第一部分相同:
在windows下编译命令为
```
cl main.c great_module.c -ic:\python27\include c:\python27\libs\python27.lib
```
在linux下编译命令为
```
gcc main.c great_module.c -o main -i/usr/include/python2.7/ -lpython2.7
```
这个例子中我们使用了python的动态类型特性。如果你想指定类型,可以利用cython的静态类型关键字。例子如下:
```
#great_module.pyx
cdef public char great_function(const char * a,int index):
return a[index]
```
cython编译后得到的.h里,great_function的声明是这样的:
```
__pyx_extern_c dl_import(char) great_function(char const *, int);
```
很开心对不对!
这样的话,我们的main函数已经几乎看不到python的痕迹了:
```
//main.c
#include <python.h>
#include "great_module.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
py_initialize();
initgreat_module();
printf("%c",great_function("hello",2));
py_finalize();
}
```
在这一部分的最后我们给一个看似实用的应用(仅限于windows):
还是利用刚才的great_module.pyx,准备一个dllmain.c:
```
#include <python.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "great_module.h"
extern __declspec(dllexport) int __stdcall _great_function(const char * a, int b) {
return great_function(a,b);
}
bool winapi dllmain(hinstance hinstdll,dword fdwreason,lpvoid lpreserved) {
switch( fdwreason ) {
case dll_process_attach:
py_initialize();
initgreat_module();
break;
case dll_process_detach:
py_finalize();
break;
}
return true;
}
```
在visual studio命令提示符下编译:
```
cl /ld dllmain.c great_module.c -ic:\python27\include c:\python27\libs\python27.lib
```
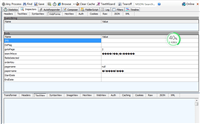
会得到一个dllmain.dll。我们在excel里面使用它,没错,传说中的**excel与python混合编程**:
<noscript><img data-rawheight="797" data-rawwidth="1007" src="https://pic2.zhimg.com/50/2f45c9f2f8407d46f51f203efc2e8181_hd.jpg" class="origin_image zh-lightbox-thumb" width="1007" src="https://pic2.zhimg.com/2f45c9f2f8407d46f51f203efc2e8181_r.jpg"/></noscript>

参考资料:cython的官方文档,质量非常高:
[welcome to cython’s documentation](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3a//docs.cython.org/)
**4 python调用c/c++(使用swig)**
用c/c++对脚本语言的功能扩展是非常常见的事情,python也不例外。除了swig,市面上还有若干用于python扩展的工具包,比较知名的还有boost.python、sip等,此外,cython由于可以直接集成c/c++代码,并方便的生成python模块,故也可以完成扩展python的任务。
答主在这里选用swig的一个重要原因是,它不仅可以用于python,也可以用于其他语言。如今swig已经支持c/c++的好基友java,主流脚本语言python、perl、ruby、php、javascript、tcl、lua,还有go、c#,以及r。swig是基于配置的,也就是说,原则上一套配置改变不同的编译方法就能适用各种语言(当然,这是理想情况了……)
swig的安装方便,有windows的预编译包,解压即用,绿色健康。主流linux通常集成swig的包,也可以下载源代码自己编译,swig非常小巧,通常安装不会出什么问题。
用swig扩展python,你需要有一个待扩展的c/c++库。这个库有可能是你自己写的,也有可能是某个项目提供的。这里举一个不浮夸的例子:希望在python中用到sse4指令集的crc32指令。
首先打开指令集的文档:[https://software.intel.com/en-us/node/514245](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3a//software.intel.com/en-us/node/514245)
可以看到有6个函数。分析6个函数的原型,其参数和返回值都是简单的整数。于是书写swig的配置文件(为了简化起见,未包含2个64位函数):
```
/* file: mymodule.i */
%module mymodule
%{
#include "nmmintrin.h"
%}
int _mm_popcnt_u32(unsigned int v);
unsigned int _mm_crc32_u8 (unsigned int crc, unsigned char v);
unsigned int _mm_crc32_u16(unsigned int crc, unsigned short v);
unsigned int _mm_crc32_u32(unsigned int crc, unsigned int v);
```
接下来使用swig将这个配置文件编译为所谓python module wrapper
```
swig -python mymodule.i
```
得到一个 mymodule_wrap.c和一个mymodule.py。把它编译为python扩展:
windows:
```
cl /ld mymodule_wrap.c /o _mymodule.pyd -ic:\python27\include c:\python27\libs\python27.lib
```
linux:
```
gcc -fpic -shared mymodule_wrap.c -o _mymodule.so -i/usr/include/python2.7/ -lpython2.7
```
注意输出文件名前面要加一个下划线。
现在可以立即在python下使用这个module了:
```
>>> import mymodule
>>> mymodule._mm_popcnt_u32(10)
2
```
回顾这个配置文件分为3个部分:
1. 定义module名称mymodule,通常,module名称要和文件名保持一致。
2. %{ %} 包裹的部分是c语言的代码,这段代码会原封不动的复制到mymodule_wrap.c
3. 欲导出的函数签名列表。直接从头文件里复制过来即可。
还记得本文第2节的那个great_function吗?有了swig,事情就会变得如此简单:
```
/* great_module.i */
%module great_module
%{
int great_function(int a) {
return a + 1;
}
%}
int great_function(int a);
```
换句话说,swig自动完成了诸如python类型转换、module初始化、导出代码表生成的诸多工作。
对于c++,swig也可以应对。例如以下代码有c++类的定义:
```
//great_class.h
#ifndef great_class
#define great_class
class great {
private:
int s;
public:
void setwall (int _s) {s = _s;};
int getwall () {return s;};
};
#endif // great_class
```
对应的swig配置文件
```
/* great_class.i */
%module great_class
%{
#include "great_class.h"
%}
%include "great_class.h"
```
这里不再重新敲一遍class的定义了,直接使用swig的%include指令
swig编译时要加-c++这个选项,生成的扩展名为cxx
```
swig -c++ -python great_class.i
```
windows下编译:
```
cl /ld great_class_wrap.cxx /o _great_class.pyd -ic:\python27\include c:\python27\libs\python27.lib
```
linux,使用c++的编译器
```
g++ -fpic -shared great_class_wrap.cxx -o _great_class.so -i/usr/include/python2.7/ -lpython2.7
```
在python交互模式下测试:
```
>>> import great_class
>>> c = great_class.great()
>>> c.setwall(5)
>>> c.getwall()
5
```
也就是说c++的class会直接映射到python class
swig非常强大,对于python接口而言,简单类型,甚至指针,都无需人工干涉即可自动转换,而复杂类型,尤其是自定义类型,swig提供了typemap供转换。而一旦使用了typemap,配置文件将不再在各个语言当中通用。
**参考资料:**
swig的官方文档,质量比较高。[swig users manual](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3a//www.swig.org/doc3.0/contents.html%23contents)
有个对应的中文版官网,很多年没有更新了。
**写在最后:**
由于cpython自身的结构设计合理,使得python的c/c++扩展非常容易。如果打算快速完成任务,cython(c/c++调用python)和swig(python调用c/c++)是很不错的选择。但是,一旦涉及到比较复杂的转换任务,无论是继续使用cython还是swig,仍然需要学习python源代码。
本文使用的开发环境:
python 2.7.10
cython 0.22
swig 3.0.6
windows 10 x64 rtm
centos 7.1 amd 64
mac osx 10.10.4
文中所述原理与具体环境适用性强。
文章所述代码均用于演示,缺乏必备的异常检查
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复

Python 实现将numpy中的nan和inf,nan替换成对应的均值
python爬虫把url链接编码成gbk2312格式过程解析

网友评论