神经侠侣演员表,免费领流量,搜索导航
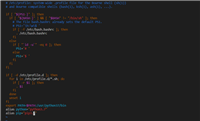
06namelist = ['well','tom'] nl = namelist ##does not copy the list #instead, assignment makes the two variables point to the one list in memory.
list = [] ## start as the empty list
list.append('a') ## use append() to add elements
list.append('b') list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] print list[1:-1] ## ['b', 'c'] list[0:2] = 'z' ## replace ['a', 'b'] with ['z'] print list ## ['z', 'c', 'd']
for var in list #遍历一个列表 value in collection #测试集合中是否存在一个值
list常用方法:
list.append(elem) #-- adds a single element to the end of the list. common error: does not return the new list, just modifies the original. list.insert(index, elem) #-- inserts the element at the given index, shifting elements to the right. list.extend(list2) #adds the elements in list2 to the end of the list. using + or += on a list is similar to using extend(). list.index(elem) -- #searches for the given element from the start of the list and returns its index. throws a valueerror if the element does not appear (use "in" to check without a valueerror). list.remove(elem) -- #searches for the first instance of the given element and removes it (throws valueerror if not present) list.sort() -- #sorts the list in place (does not return it). (the sorted() function shown below is preferred.) list.reverse() -- #reverses the list in place (does not return it) list.pop(index) -- #removes and returns the element at the given index. returns the rightmost element if index is omitted (roughly the opposite of append()).
# c. sort_last
# given a list of non-empty tuples, return a list sorted in increasing
# order by the last element in each tuple.
# e.g. [(1, 7), (1, 3), (3, 4, 5), (2, 2)] yields
# [(2, 2), (1, 3), (3, 4, 5), (1, 7)]
# hint: use a custom key= function to extract the last element form each tuple.
def last(a): return a[-1] def sort_last(tuples): # +++your code here+++ return sorted(tuples,key=last)
def linear_merge(list1, list2): # +++your code here+++ # lab(begin solution) result = [] # look at the two lists so long as both are non-empty. # take whichever element [0] is smaller. while len(list1) and len(list2): if list1[0]
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
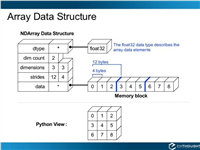

Python 实现将numpy中的nan和inf,nan替换成对应的均值
python爬虫把url链接编码成gbk2312格式过程解析

网友评论