淘宝查号网址,亚冠半决赛时间,宝安南国影城
本文实例讲述了python实现的数据结构与算法之基本搜索。分享给大家供大家参考。具体分析如下:
一、顺序搜索
顺序搜索 是最简单直观的搜索方法:从列表开头到末尾,逐个比较待搜索项与列表中的项,直到找到目标项(搜索成功)或者 超出搜索范围 (搜索失败)。
根据列表中的项是否按顺序排列,可以将列表分为 无序列表 和 有序列表。对于 无序列表,超出搜索范围 是指越过列表的末尾;对于 有序列表,超过搜索范围 是指进入列表中大于目标项的区域(发生在目标项小于列表末尾项时)或者指越过列表的末尾(发生在目标项大于列表末尾项时)。
1、无序列表
在无序列表中进行顺序搜索的情况如图所示:

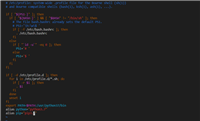
def sequentialsearch(items, target):
for item in items:
if item == target:
return true
return false
2、有序列表
在有序列表中进行顺序搜索的情况如图所示:

def orderedsequentialsearch(items, target):
for item in items:
if item == target:
return true
elif item > target:
break
return false
二、二分搜索
实际上,上述orderedsequentialsearch算法并没有很好地利用有序列表的特点。
二分搜索 充分利用了有序列表的优势,该算法的思路非常巧妙:在原列表中,将目标项(target)与列表中间项(middle)进行对比,如果target等于middle,则搜索成功;如果target小于middle,则在middle的左半列表中继续搜索;如果target大于middle,则在middle的右半列表中继续搜索。
在有序列表中进行二分搜索的情况如图所示:

根据实现方式的不同,二分搜索算法可以分为迭代版本和递归版本两种:
1、迭代版本
def iterativebinarysearch(items, target):
first = 0
last = len(items) - 1
while first <= last:
middle = (first + last) // 2
if target == items[middle]:
return true
elif target < items[middle]:
last = middle - 1
else:
first = middle + 1
return false
2、递归版本
def recursivebinarysearch(items, target):
if len(items) == 0:
return false
else:
middle = len(items) // 2
if target == items[middle]:
return true
elif target < items[middle]:
return recursivebinarysearch(items[:middle], target)
else:
return recursivebinarysearch(items[middle+1:], target)
三、性能比较
上述搜索算法的时间复杂度如下所示:
搜索算法 时间复杂度 ----------------------------------- sequentialsearch o(n) ----------------------------------- orderedsequentialsearch o(n) ----------------------------------- iterativebinarysearch o(log n) ----------------------------------- recursivebinarysearch o(log n) ----------------------------------- in o(n)
可以看出,二分搜索 的性能要优于 顺序搜索。
值得注意的是,python的成员操作符 in 的时间复杂度是o(n),不难猜出,操作符 in 实际采用的是 顺序搜索 算法。
四、算法测试
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def test_print(algorithm, listname, target):
print(' %d is%s in %s' % (target, '' if algorithm(eval(listname), target) else ' not', listname))
if __name__ == '__main__':
testlist = [1, 2, 32, 8, 17, 19, 42, 13, 0]
orderedlist = sorted(testlist)
print('sequentialsearch:')
test_print(sequentialsearch, 'testlist', 3)
test_print(sequentialsearch, 'testlist', 13)
print('orderedsequentialsearch:')
test_print(orderedsequentialsearch, 'orderedlist', 3)
test_print(orderedsequentialsearch, 'orderedlist', 13)
print('iterativebinarysearch:')
test_print(iterativebinarysearch, 'orderedlist', 3)
test_print(iterativebinarysearch, 'orderedlist', 13)
print('recursivebinarysearch:')
test_print(recursivebinarysearch, 'orderedlist', 3)
test_print(recursivebinarysearch, 'orderedlist', 13)
运行结果:
$ python testbasicsearch.py sequentialsearch: 3 is not in testlist 13 is in testlist orderedsequentialsearch: 3 is not in orderedlist 13 is in orderedlist iterativebinarysearch: 3 is not in orderedlist 13 is in orderedlist recursivebinarysearch: 3 is not in orderedlist 13 is in orderedlist
希望本文所述对大家的python程序设计有所帮助。
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复

Python 实现将numpy中的nan和inf,nan替换成对应的均值
python爬虫把url链接编码成gbk2312格式过程解析

网友评论