天竺山森林公园好玩吗,山水藏龙bbs,路灯节电
okhttp是一款高效的http客户端,支持连接同一地址的链接共享同一个socket,通过连接池来减小响应延迟,还有透明的gzip压缩,请求缓存等优势。(github页:https://github.com/square/okhttp)
android为我们提供了两种http交互的方式:httpurlconnection 和 apache http client,虽然两者都支持https,流的上传和下载,配置超时,ipv6和连接池,已足够满足我们各种http请求的需求。但更高效的使用http 可以让您的应用运行更快、更节省流量。而okhttp库就是为此而生。
okhttp是一个高效的http库:
如果您的服务器配置了多个ip地址,当第一个ip连接失败的时候,okhttp会自动尝试下一个ip。okhttp还处理了代理服务器问题和ssl握手失败问题。
使用 okhttp 无需重写您程序中的网络代码。okhttp实现了几乎和java.net.httpurlconnection一样的api。如果您用了 apache httpclient,则okhttp也提供了一个对应的okhttp-apache 模块。
引入
可以通过下载jar包直接导入工程地址
或者通过构建的方式导入
maven:
<dependency> <groupid>com.squareup.okhttp</groupid> <artifactid>okhttp</artifactid> <version>2.4.0</version> </dependency>
gradle:
compile 'com.squareup.okhttp:okhttp:2.4.0'
package com.jackchan.test.okhttptest;
import android.os.bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.actionbaractivity;
import android.util.log;
import com.squareup.okhttp.cache;
import com.squareup.okhttp.callback;
import com.squareup.okhttp.okhttpclient;
import com.squareup.okhttp.request;
import com.squareup.okhttp.response;
import java.io.file;
import java.io.ioexception;
public class testactivity extends actionbaractivity {
private final static string tag = "testactivity";
private final okhttpclient client = new okhttpclient();
@override
protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate);
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_test);
new thread(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
try {
execute();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
public void execute() throws exception {
request request = new request.builder()
.url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt")
.build();
response response = client.newcall(request).execute();
if(response.issuccessful()){
system.out.println(response.code());
system.out.println(response.body().string());
}
}
}
private void enqueue(){
request request = new request.builder()
.url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt")
.build();
client.newcall(request).enqueue(new callback() {
@override
public void onfailure(request request, ioexception e) {
}
@override
public void onresponse(response response) throws ioexception {
//not ui thread
if(response.issuccessful()){
system.out.println(response.code());
system.out.println(response.body().string());
}
}
});
}
request request = new request.builder()
.url("https://api.github.com/repos/square/okhttp/issues")
.header("user-agent", "okhttp headers.java")
.addheader("accept", "application/json; q=0.5")
.addheader("accept", "application/vnd.github.v3+json")
.build();
requestbody formbody = new formencodingbuilder()
.add("platform", "android")
.add("name", "bug")
.add("subject", "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx")
.build();
request request = new request.builder()
.url(url)
.post(body)
.build();
response response = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (response.issuccessful()) {
return response.body().string();
} else {
throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response);
}
package com.jackchan.test.okhttptest;
import android.os.bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.actionbaractivity;
import android.util.log;
import com.squareup.okhttp.cache;
import com.squareup.okhttp.cachecontrol;
import com.squareup.okhttp.call;
import com.squareup.okhttp.callback;
import com.squareup.okhttp.okhttpclient;
import com.squareup.okhttp.request;
import com.squareup.okhttp.response;
import java.io.file;
import java.io.ioexception;
public class testactivity extends actionbaractivity {
private final static string tag = "testactivity";
private final okhttpclient client = new okhttpclient();
@override
protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate);
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_test);
file sdcache = getexternalcachedir();
int cachesize = 10 * 1024 * 1024; // 10 mib
client.setcache(new cache(sdcache.getabsolutefile(), cachesize));
new thread(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
try {
execute();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
public void execute() throws exception {
request request = new request.builder()
.url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt")
.build();
response response1 = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (!response1.issuccessful()) throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response1);
string response1body = response1.body().string();
system.out.println("response 1 response: " + response1);
system.out.println("response 1 cache response: " + response1.cacheresponse());
system.out.println("response 1 network response: " + response1.networkresponse());
response response2 = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (!response2.issuccessful()) throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response2);
string response2body = response2.body().string();
system.out.println("response 2 response: " + response2);
system.out.println("response 2 cache response: " + response2.cacheresponse());
system.out.println("response 2 network response: " + response2.networkresponse());
system.out.println("response 2 equals response 1? " + response1body.equals(response2body));
}
}
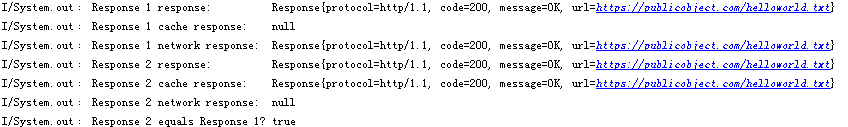
public void execute() throws exception {
request request = new request.builder()
.url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt")
.build();
response response1 = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (!response1.issuccessful()) throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response1);
string response1body = response1.body().string();
system.out.println("response 1 response: " + response1);
system.out.println("response 1 cache response: " + response1.cacheresponse());
system.out.println("response 1 network response: " + response1.networkresponse());
request = request.newbuilder().cachecontrol(cachecontrol.force_network).build();
response response2 = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (!response2.issuccessful()) throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response2);
string response2body = response2.body().string();
system.out.println("response 2 response: " + response2);
system.out.println("response 2 cache response: " + response2.cacheresponse());
system.out.println("response 2 network response: " + response2.networkresponse());
system.out.println("response 2 equals response 1? " + response1body.equals(response2body));
}
request = request.newbuilder().cachecontrol(cachecontrol.force_network).build();

protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate);
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_test);
file sdcache = getexternalcachedir();
int cachesize = 10 * 1024 * 1024; // 10 mib
//client.setcache(new cache(sdcache.getabsolutefile(), cachesize));
new thread(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
try {
execute();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
system.out.println(e.getmessage().tostring());
}
}
}).start();
}
public void execute() throws exception {
request request = new request.builder()
.url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt")
.build();
response response1 = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (!response1.issuccessful()) throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response1);
string response1body = response1.body().string();
system.out.println("response 1 response: " + response1);
system.out.println("response 1 cache response: " + response1.cacheresponse());
system.out.println("response 1 network response: " + response1.networkresponse());
request = request.newbuilder().cachecontrol(cachecontrol.force_cache).build();
response response2 = client.newcall(request).execute();
if (!response2.issuccessful()) throw new ioexception("unexpected code " + response2);
string response2body = response2.body().string();
system.out.println("response 2 response: " + response2);
system.out.println("response 2 cache response: " + response2.cacheresponse());
system.out.println("response 2 network response: " + response2.networkresponse());
system.out.println("response 2 equals response 1? " + response1body.equals(response2body));
}

public void canceltest() throws exception {
request request = new request.builder()
.url("http://httpbin.org/delay/2") // this url is served with a 2 second delay.
.build();
final long startnanos = system.nanotime();
final call call = client.newcall(request);
// schedule a job to cancel the call in 1 second.
executor.schedule(new runnable() {
@override
public void run() {
system.out.printf("%.2f canceling call.%n", (system.nanotime() - startnanos) / 1e9f);
call.cancel();
system.out.printf("%.2f canceled call.%n", (system.nanotime() - startnanos) / 1e9f);
}
}, 1, timeunit.seconds);
try {
system.out.printf("%.2f executing call.%n", (system.nanotime() - startnanos) / 1e9f);
response response = call.execute();
system.out.printf("call is cancel:" + call.iscanceled() + "%n");
system.out.printf("%.2f call was expected to fail, but completed: %s%n",
(system.nanotime() - startnanos) / 1e9f, response);
} catch (ioexception e) {
system.out.printf("%.2f call failed as expected: %s%n",
(system.nanotime() - startnanos) / 1e9f, e);
}
}


如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
Android apk 项目一键打包并上传到蒲公英的实现方法
Android 自定义LineLayout实现满屏任意拖动功能的示例代码
android 限制某个操作每天只能操作指定的次数(示例代码详解)
Android 集成 google 登录并获取性别等隐私信息的实现代码
网友评论