韩佳简历,重庆房价走势2013,白芝麻价格
目录
flask是一个轻量级的可定制框架,使用python语言编写,较其他同类型框架更为灵活、轻便、安全且容易上手。
它可以很好地结合mvc模式进行开发,开发人员分工合作,小型团队在短时间内就可以完成功能丰富的中小型网站或web服务的实现。
另外,flask还有很强的定制性,用户可以根据自己的需求来添加相应的功能,在保持核心功能简单的同时实现功能的丰富与扩展,
其强大的插件库可以让用户实现个性化的网站定制,开发出功能强大的网站。
#安装flask
- pip3 install flask - 1.1.1
flask库文件(安装flask时自动安装)
- jinja2 模板渲染库
- markupsafe 返回安全标签 只要flask 返回模板或者标签时都会依赖markupsafe
- werkzeug 德文“工具” == uwsgi 底层是 wsgi flask项目启动都是基于werkzeug

django 框架 - 原生组件非常丰富 教科书式框架 - django.model - orm 面向对象操作数据库 - django.form form组件 - django.modelform modelform - django.session model session - admin csrftoken 跨站请求伪造 django框架(缺点) 加载项巨大 资源浪费 django框架 适合大型,密集型项目 flask web框架 - flask 非常短小精悍 - 精简到只有一个 session flask 第三方组件 非常全 flask框架(缺点) 第三方组件 - 运行稳定性相对较差 flask框架 适合小型,api服务类项目
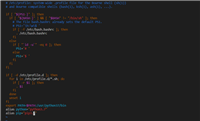
# 三行启动flask 提供服务 from flask import flask app = flask(__name__) app.run() #访问一下看看效果

# 启动flask 提供服务,访问返回页面,"helloworld"
from flask import flask # 导入flask 类创建flask应用对象
app = flask(__name__) # app = application
@app.route("/index") # 为 flask 应用对象增加路由
def index(): # 与路由绑定的视图函数 视图函数名尽可能保持唯一
return "helloworld" # “” 相当于 django 中的 httpresponse
if __name__ == '__main__': # 当前文件处于脚本状态时运行如下代码
app.run() # 启动flask 应用
#访问一下看看效果

@app.route("/index")
def index():
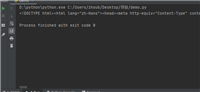
return "helloworld" # "helloworld" 相当于 django中的httpresponse返回响应 (效果如上图)

#html代码
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>郭楷丰</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>你好</h1>
</body>
</html>
#python代码
from flask import flask, render_template
app = flask(__name__)
@app.route("/home")
def home():
return render_template("home.html") # 模板存放路径 templates
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
#访问一下看看效果

from flask import flask, render_template, redirect
app = flask(__name__)
@app.route("/home")
def home():
return render_template("home.html")
@app.route("/re")
def re():
return redirect("/home") #重定向到home
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
#访问一下看看效果


小结:
# 3xx http status
# 4xx 错误 客户端
# 5xx 错误 服务器
redirect("/home") 其实就是在responseheaders 中加入了一个 location:http://127.0.0.1:5000/home
#返回图片示例 代码
#先准备一张图片 1.jpg
from flask import flask,send_file
app = flask(__name__)
@app.route("/get_file")
def get_file():
return send_file("1.jpg")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
#访问一下试试看

小结: # 打开并返回文件内容 自动识别文件类型 在responseheaders中加入 # content-type:文件类型 - *文件类型 是可以被客户端识别的文件类型(如mp4,mp3,文本,图片等) # 不能识别的类型 下载处理 - 浏览器会下载
from flask import flask, jsonify
app = flask(__name__)
@app.route("/get_json")
def get_json():
d = {
"name": "gkf"
}
return jsonify(d)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
#访问一下试试看

小结:
jsonify("字符串或数据类型") 返回标准格式的json字符串
# content-type:application/json == 标准格式
# flask 1.1.1 目前版本 支持return d 使用
# return d # 暂时不建议使用 兼容性差
# 直接返回dict时 本质上在执行jsonify(d)
jsonify()做了那些事
# 1.打包json 序列化json字符串
# 2.编写responseheaders 加入 content-type:application/json
应用场景:
# api 接口 ajax.post({username:123}){function(data){ obj = data }}
#可以判断客户端的请求来做一些操作
@app.route("/index")
def index():
print(request.method)
if request.method == 'get': #如果是get请求,返回一个文件
return render_template("")

#html代码
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<p>username: <input type="text" name="username"></p>
<p><input type="file" name="my_file"></p>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
#python代码
def login():
if request.method == 'get':
return render_template('login.html')
if request.method == 'post':
print(request.form.get("username")) #直接获取到username对应的值
return redirect("/index")

#代码
@app.route("/index")
def index():
if request.method == 'get':
print(request.args) #request.args.get('键') 来取值
return render_template("")

@app.route("/index")
def index():
if request.method == 'get':
print(request.url)
return render_template("")
#当页面输入 http://127.0.0.1:5000/index 打印结果
http://127.0.0.1:5000/index
#当页面输入 http://127.0.0.1:5000/index?郭楷丰=318 打印结果
http://127.0.0.1:5000/index?郭楷丰=318
@app.route("/index")
def index():
if request.method == 'get':
print(request.url_charset)
return render_template("")
#打印结果
utf-8
# print(request.url_root) # 请求地址 完整请求地址 host
@app.route("/index")
def index():
if request.method == 'get':
print(request.url_root)
return render_template("")
#访问http://127.0.0.1:5000/index 打印结果
http://127.0.0.1:5000/
print(request.url_rule) # 请求路由地址(参数不会获取) #访问http://127.0.0.1:5000/index 打印结果 /index
#接收所有(get,post)请求中的数据,包含了 url 和 formdata 中的数据
#一般不使用这个 因为url中的参数和form表的的参数它都会获取,如果key值重名,会报错
print(request.values)
#访问http://127.0.0.1:5000/index?郭楷丰=318 打印结果
combinedmultidict([immutablemultidict([('郭楷丰', '318')]), immutablemultidict([])])
#to_dict 转为字典形式
print(request.values.to_dict())
#访问http://127.0.0.1:5000/index?郭楷丰=318 打印结果
{'郭楷丰': '318'}
@app.route("/login",methods=["get","post"]) #重新methods让它只接受"get","post"请求
def login():
if request.method == 'get':
return render_template('login.html')
if request.method == 'post':
print(request.files)
print(request.files.get("my_file"))
return redirect("/index")
#访问http://127.0.0.1:5000/login 并提交一个文件 执行结果
immutablemultidict([('my_file', <filestorage: '1_副本.png' ('image/png')>)])
<filestorage: '1_副本.png' ('image/png')> #获取文件名字
#upload.html文件代码
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>文件上传演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<p><input type="file" name="my_file"></p>
<input type="submit" value="上传图片">
</form>
</body>
</html>
#python代码
import os
from flask import flask, request, render_template
app = flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = "!@#$%^&*()" #密钥(对session进行加密)
app.debug = true #开启debug模式 修改代码自动重启项目
@app.route("/upload",methods=["get","post"])#重写methods只接收get与post请求
def upload():
if request.method == 'get':
return render_template('upload.html')
if request.method == 'post':
dir_name = './美女图片'
if not os.path.exists(dir_name):
os.mkdir(dir_name)
my_file = request.files.get("my_file")
new_file = os.path.join(dir_name, my_file.filename)
my_file.save(new_file)
return "上传文件成功"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()


# 获取其他数据 # request.headers 请求头中的信息 # request.cookies 请求中cookies的信息 # request.path == request.url_rule 路由地址 # request.host == "127.0.0.1:9527" 获取访问主机地址 # request.host_url == "http://127.0.0.1:9527/" 路由地址 # 特殊提交方式数据获取 # request.json 获取content-type:application/json时提交的数据 # content-type:application/json # request.data 获取 原始请求体中的数据 b""类型 # content-type 无法被识别 或 不包含form字眼
#python代码
from flask import flask, render_template
#传给模板的数据
student = {'name': 'old', 'age': 38, 'gender': '中'}
student_list = [
{'name': 'old', 'age': 38, 'gender': '中'},
{'name': 'boy', 'age': 73, 'gender': '男'},
{'name': 'edu', 'age': 84, 'gender': '女'}
]
student_dict = {
1: {'name': 'old', 'age': 38, 'gender': '中'},
2: {'name': 'boy', 'age': 73, 'gender': '男'},
3: {'name': 'edu', 'age': 84, 'gender': '女'},
}
app = flask(__name__)
app.debug = true
@app.template_global()
def ab(a, b):
return a + b
@app.route("/stu")
def stu():
return render_template("stuinfo.html", stu_info=student, stu_list=student_list, stu_dict=student_dict)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
<!--stuinfo.html模板代码-->
<!doctype html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<title>学生信息</title>
<style type='text/css'>
p{
background-color:#00ffaa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
{{ stu_info }}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td>age</td>
<td>gender</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>{{ stu_info.name }}</td>
<td>{{ stu_info.get("age") }}</td>
<td>{{ stu_info["gender"] }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
{{ stu_list }}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td>age</td>
<td>gender</td>
</tr>
{% for stu in stu_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ stu.name }}</td>
<td>{{ stu.get("age") }}</td>
<td>
{% if stu["gender"] != "男" and stu["gender"] != "女" %}
李杰
{% else %}
{{ stu["gender"] }}
{% endif %}
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
{{ stu_dict }}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
{% for foo in stu_dict %}
{{ stu_dict[foo].get("name") }}
{{ stu_dict[foo]["age"] }}
{{ stu_dict[foo].gender }}
{% endfor %}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
{% for foo,item in stu_dict.items() %}
{{ foo }}
{{ item.name }}
{% endfor %}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
{{ ab(666,2) }}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
{% macro my_input(ty,na) %}
请输入用户名 -> <input type="{{ ty }}" name="{{ na }}">
{% endmacro %}
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
<p>这就是我自己创造的input标签:{{ my_input("text","username") }} {{ my_input("password","pass") }} {{ my_input("file","myfile") }}</p>
<p>- - - - - - - -✂ - - - - - - - - - - - -分割线- - - - - - - - - - - -✂- - - - - - - -</p>
</body>
</html>




我的博客即将同步至腾讯云+社区,邀请大家一同入驻:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/support-plan?invite_code=2ky0wzouug4kk
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复

Python 实现将numpy中的nan和inf,nan替换成对应的均值
python爬虫把url链接编码成gbk2312格式过程解析

网友评论