第五季影院,国语动画,义乌韩国饰品批发网
给出一个$n \times m$的网格,每个位置有一个小写字母,初始在$(1, 1)$,每次可以向上下左右走,问走到$(n, m)$的最小花费
设$(x, y)$为当前位置,$(nx, ny)$为下一位置。$s[x][y]$表示$(x, y)$位置的字符。
若$s[x][y] = s[nx][ny]$,则移动的花费为$0$,否则花费为$1$
01BFS的裸题,感觉这个点子还是很妙的
01BFS可以在$O(n+m)$求出边权只有$0 / 1$的最短路
我们维护一个双端队列,如当前可以进行松弛那么就进行更新,更新完后判断一下,若边权为$1$,则在队尾加入下一个点,否则在队首加入下一个点
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1001;
inline int read() {
char c = getchar(); int x = 0, f = 1;
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar();
return x * f;
}
int N, M;
struct Node {
int x, y, s;
};
deque<Node> q;
int dis[MAXN][MAXN], xx[] = {-1, +1, 0, 0}, yy[] = {0, 0, -1, +1};
char s[MAXN][MAXN];
void OneZeroBFS() {
q.push_back((Node) {1, 1, 0});
while(!q.empty()) {
Node p = q.front(); q.pop_front();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int wx = p.x + xx[i], wy = p.y + yy[i];
int w = (s[wx][wy] != s[p.x][p.y]);
if(dis[wx][wy] > dis[p.x][p.y] + w && (wx > 0 && wy > 0 && wx <= N && wy <= M))
dis[wx][wy] = dis[p.x][p.y] + w,
w == 1 ? q.push_back((Node) {wx, wy, w}) : q.push_front((Node) {wx, wy, w});
}
}
}
main() {
int QwQ = read();
while(QwQ--) {
memset(dis, 0xf, sizeof(dis));
dis[1][1] = 0;
N = read(); M = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
scanf("%s", s[i] + 1);
OneZeroBFS();
printf("%d\n", dis[N][M]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
4
2 2
aa
aa
2 3
abc
def
6 6
akaccc
aaacfc
amdfcc
aokhdd
zyxwdp
zyxwdd
5 5
abbbc
abacc
aaacc
aefci
cdgdd
*/
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
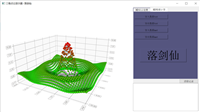
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论