北京哪里做双眼皮好,淡淡的感觉,郏县邮编
c++的构造函数属性初始化_静态成员_this指针代码实例讲解
#include using namespace std;
//构造函数的属性初始化列表
/*class teacher{
private:
char* name;
public:
teacher(char* name){
this->name = name;
}
char* getname(){
return this->name;
}
};
class student{
private:
char* name;
//对象属性该如何赋值
teacher t1;
teacher t2;
public:
student(char* name, char* name_t1, char* name_t2) :t1(name_t1), t2(name_t2){
this->name = name;
cout << "studnet构造函数" << endl;
}
void my_print(){
cout << this->name << "," << t1.getname() << "," << t2.getname() << endl;
}
};
void main(){
student t("tom", "bo", "c");
t.my_print();
system("pause");
}*/
//c++ 通过new(delete)动态内存分配
//cmalloc(free)
/*class teacher{
public:
char* name;
int age;
public:
teacher(char* name, int age){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
cout << "有参构造函数" << endl;
}
~teacher(){
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
};
void main(){
//c++ (new delete)动态内存分配
//对象
//分配内存,调用了构造函数
teacher* t1 = new teacher("tom", 20);
//释放内存,调用了析构函数
delete t1;
//数组
int* i2 = new int[10];
delete[] i2;
//c 动态内存分配
//对象
teacher* t3 = (teacher*)malloc(sizeof(teacher));
free(t3);
//数组
int* t4 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)* 10);
t4[2] = 6;
free(t4);
system("pause");
}*/
/*静态属性 方法
class student{
public:
char* name;
//静态属性
static int total;
public:
student(char* name){
this->name = name;
cout << "构造函数" << endl;
}
~student(){
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
//非静态方法可以调用静态属性
void count(){
total++;
cout << total << endl;
}
//静态方法中只能调用静态属性
static void count2(){
total++;
cout << total << endl;
}
};
//给静态属性赋值
int student::total = 6;
void main(){
//通过 类名::静态属性名 方法调用类中的静态属性
//cout << student::total << endl;
//通过 类名::静态方法() 调用静态方法
student::count2();
//student t1("jack");
//t1.count();
system("pause");
}*/
//类的大小
/*class a{
public:
int i;
int j;
int k;
static int m;
};
class b{
public:
int i;
int j;
int k;
void myprintf(){
cout << "打印" << endl;
}
};
void main(){
cout << sizeof(a) << endl;//12
cout << sizeof(b) << endl;//12
//可以看到静态属性和非静态属性不在同一内存
system("pause");
}*/
/*
//常函数,当前对象不能被修改,防止数据成员被非法访问
class student{
public:
char* name;
public:
student(char* name){
this->name = name;
cout << "构造函数" << endl;
}
//常函数
//既不能改变指针的值,又不能改变指针指向的内容
//const teacher* const this
void print() const{
//下面两句会报错
//this->name = "tom";
//this = (student*)0x0011;
printf("%#x", this);
cout << this->name << "," << endl;
}
void print2(){
printf("%#x", this);
cout << this->name << "," << endl;
}
};
void main(){
student t1("tom");
const student t2("jack");
//常量对象只能调用常量方法
t2.print();
//下面这句会报错
//t2.print2();
//非常量对象既可以调用常量方法,也可以调用非常量方法
t1.print();
t1.print2();
system("pause");
}*/
/*
class a{
//友元函数
friend void change(a* a, int b);
private:
int i;
public:
a(int i){
this->i = i;
}
void print(){
cout << i << endl;
}
};
//友元函数的实现,在友元函数中可以访问私有的属性
void change(a* a, int b){
a->i = b;
}
void main(){
a a(5);
a.print();
change(&a, 10);
a.print();
system("pause");
}*/
//友元类
/*
class a{
//声明友元类 友元类可以访问a类中的所有属性
friend class b;
private:
int i;
public:
a(int i){
this->i = i;
}
void print(){
cout << i << endl;
}
};
class b{
private:
a a;
public:
void change(){
a.i = 20;
}
};
*/
//运算符重载
/*
class point{
public:
int x;
int y;
public:
point(int x = 0, int y = 0){
this->x = x;
this -> y = y;
}
void print(){
cout << x << "," << y << endl;
}
};
//运算符重载如果放在类外面,则需要两个参数
//这里使用的是引用,不是指针,要比指针方便
point operator+(point &p1, point &p2){
point tmp(p1.x + p2.x, p1.y + p2.y);
return tmp;
}
point operator-(point &p1, point &p2){
point tmp(p1.x - p2.x, p1.y - p2.y);
return tmp;
}
void main(){
point p1(3, 4);
point p2(1, 2);
point p3=p1 - p2;
p3.print();
system("pause");
}*/
//成员函数,运算符重载
//如果要在函数内部进行重载,则参数只能有一个
/*class point{
public:
int x;
int y;
public:
point(int x = 0, int y = 0){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void print(){
cout << x << "," << y << endl;
}
point operator+( point &p){
point tmp(this->x + p.x, this->y + p.y);
return tmp;
}
point operator-(point &p){
point tmp(this->x - p.x, this->y - p.y);
return tmp;
}
};
void main(){
point p1(3, 4);
point p2(1, 2);
point p3 = p1 - p2;
p3.print();
system("pause");
}*/
//当属性私有时,通过友元函数完成运算符重载
class point{
//属性私有
friend point operator+(point &p1, point &p2);
friend point operator-(point &p1, point &p2);
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
point(int x = 0, int y = 0){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void print(){
cout << x << "," << y << endl;
}
};
//运算符重载是放在类外面的
//这里使用的是引用,不是指针,要比指针方便
point operator+(point &p1, point &p2){
point tmp(p1.x + p2.x, p1.y + p2.y);
return tmp;
}
point operator-(point &p1, point &p2){
point tmp(p1.x - p2.x, p1.y - p2.y);
return tmp;
}
void main(){
point p1(3, 4);
point p2(1, 2);
point p3 = p1 - p2;
p3.print();
system("pause");
}
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
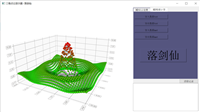
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论