鲅鱼圈站,论文之家,清雨禾
\(10^5\)次询问每次询问\(10^5\)个区间。。这种题第一感觉就是根号/数据分治的模型。
\(k\)是个定制这个很关键。
考虑\(k\)比较小的情况,可以直接暴力建sam,\(n^2\)枚举\(w\)的子串算出现次数。询问用个\(n^2\)的vector记录一下每次在vector里二分就好。
\(k\)比较大的情况我没想到什么好的做法,网上的做法复杂度也不是很好。。
然后写了个广义sam + 暴力跳parent就过了。。
不过这题思想还是很好的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define pair pair<int, int>
#define mp(x, y) make_pair(x, y)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define fin(x) {freopen(#x".in","r",stdin);}
#define fout(x) {freopen(#x".out","w",stdout);}
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 4e5 + 10, inf = 1e9 + 1, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-9, pi = acos(-1);
template <typename a, typename b> inline bool chmin(a &a, b b){if(a > b) {a = b; return 1;} return 0;}
template <typename a, typename b> inline bool chmax(a &a, b b){if(a < b) {a = b; return 1;} return 0;}
template <typename a, typename b> inline ll add(a x, b y) {if(x + y < 0) return x + y + mod; return x + y >= mod ? x + y - mod : x + y;}
template <typename a, typename b> inline void add2(a &x, b y) {if(x + y < 0) x = x + y + mod; else x = (x + y >= mod ? x + y - mod : x + y);}
template <typename a, typename b> inline ll mul(a x, b y) {return 1ll * x * y % mod;}
template <typename a, typename b> inline void mul2(a &x, b y) {x = (1ll * x * y % mod + mod) % mod;}
inline int read() {
char c = getchar(); int x = 0, f = 1;
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar();
return x * f;
}
int n, m, q, k;
char s[maxn], w[maxn];
string q[maxn];
int l[maxn], r[maxn], a[maxn], b[maxn], pos[maxn];
vector<int> line[1001][1001], v[maxn];
int ch[maxn][26], siz[maxn], len[maxn], fa[maxn], las = 1, root = 1, tot = 1;
void insert(int x, int opt) {
int now = ++tot, pre = las; las = now; len[now] = len[pre] + 1; siz[now] = opt;
for(; pre && !ch[pre][x]; pre = fa[pre]) ch[pre][x] = now;
if(!pre) fa[now] = root;
else {
int q = ch[pre][x];
if(len[pre] + 1 == len[q]) fa[now] = q;
else {
int nq = ++tot; len[nq] = len[pre] + 1; fa[nq] = fa[q];
memcpy(ch[nq], ch[q], sizeof(ch[q]));
fa[now] = fa[q] = nq;
for(; pre && ch[pre][x] == q; pre = fa[pre]) ch[pre][x] = nq;
}
}
}
void dfs(int x) {
for(auto &to : v[x]) {
dfs(to);
siz[x] += siz[to];
}
}
int query(vector<int> &q, int a, int b) {
return (upper_bound(q.begin(), q.end(), b) - lower_bound(q.begin(), q.end(), a));
}
ll solve1(int a, int b) {
ll ret = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
int now = root;
for(int j = i; j <= k; j++) {
int x = w[j] - 'a'; now = ch[now][x];
if(!now) break;
else ret += 1ll * siz[now] * query(line[i][j], a, b);
}
}
return ret;
}
void build() {
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) v[fa[i]].push_back(i);
dfs(root);
}
signed main() {
// freopen("string9.in", "r", stdin); freopen("b.out", "w", stdout);
n = read(); m = read(); q = read(); k = read();
scanf("%s", s + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(s[i] - 'a', 1);
if(k <= 1000) {
build();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) l[i] = read() + 1, r[i] = read() + 1, line[l[i]][r[i]].push_back(i);
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
scanf("%s", w + 1); int a = read() + 1, b = read() + 1;
cout << solve1(a, b) << '\n';
}
}
else {
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) l[i] = read() + 1, r[i] = read() + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
cin >> q[i]; a[i] = read() + 1, b[i] = read() + 1;
las = 1;
for(auto &x : q[i]) insert(x - 'a', 0);
}
build();
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
memset(pos, 0, sizeof(pos));
int now = root;
for(int j = 0; j < q[i].length(); j++) {
int x = q[i][j] - 'a'; now = ch[now][x];
if(!now) break;
else pos[j + 1] = now;
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int j = a[i]; j <= b[i]; j++) {
int cur = pos[r[j]];
while(len[fa[cur]] >= r[j] - l[j] + 1) cur = fa[cur];//这里可以卡掉
ans += siz[cur];
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
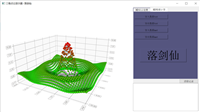
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论