计算机培训,章子怡沙滩81张图片,三星手机ce0168
随着学习的深入,就会发现曾经学的const还有更深入的用法,现在就对const的未总结的用法进行总结。
本文就是针对const在类中的情况进行的总结。
有时我们会遇到下面这种将类的成员变量用const进行修饰的情况
class coordinate
{
public:
coordinate(int x,int y);
private:
const int m_ix;
const int m_iy;
}
在这种被const修饰过的成员变量进行赋值的时候需要注意:
coordinate::coordinate(int x,int y)
{
m_ix = x;
m_iy = y;
}
这种赋值方式是错误的,需要用初始化列表,如下:
coordinate::coordinate(int x,int y):m_ix(x),m_iy(y)
{
}
当然如果这个类的成员变量的类型是另一个类,也被const修饰,如下:
class line
{
public:
line(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2);
private:
const coordinate m_coora;
const coordinate m_coorb;
}
那么,他的初始化依旧是只能使用初始化列表:
line::line(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2):
m_coora(x1,y1),m_coorb(x2,y2)
{
cout<<"line"<<endl;
}
当然,const不止能修饰成员变量,也能修饰成员函数,下面就对coordinate类进行稍作添加修改:
class coordinate
{
public:
coordinate(int x,int y);
void changex() const;
void changex();
private:
const int m_ix;
const int m_iy;
}
其中,我们重载定义了两个changex成员函数,其中一个用const修饰,那么我们需要注意下面一个问题:
void coordinate::changex() const
{
m_ix=10;//错误
}
void coordinate::changex()
{
m_ix=20;
}
被const修饰的成员函数(即常成员函数)不能改变数据成员的值,
是因为编译时会变成下面的样子
void changex(const coordinate *this)
{
this->m_ix=10;
}
会隐含着this指针,这个this指针是被const修饰的,即为常指针,这个常指针不能修改所指向的数据。
虽然这两个changex是重载的,但是一定要分清楚什么时候调用哪个。
int main(void)
{
const coordinate coordinate(3,5);//常对象
coordinate.changex();//调用的是常成员函数
return 0;
}
只有用const修饰并声明的常对象才能调用常成员函数。
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
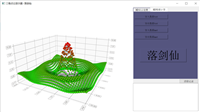
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论