克洛伊-马菲亚,我为神狂,电信dns地址
二叉树的一个重要应用是它们在查找中的使用。
二叉查找树的性质:对于树中的每个节点x,它的左子树中所有项的值小于x中的项,而它的右子树中所有项的值大于x中的项。这意味着该树所有的元素可以用某种一致的方式排序。
二叉查找树的平均深度是o(logn)。二叉查找树要求所有的项都能够排序。树中的两项总可以使用comparable接口中的compareto方法比较。
adt的声明:
struct treenode;
typedef struct treenode *position;
typedef struct treenode *searchtree;
searchtree makeempty(searchtree t);
position find(elementtype x, searchtree t);
position findmax(searchtree t);
position findmin(searchtree t);
searchtree insert(elementtype x, searchtree t);
searchtree delete(elementtype x, searchtree t);
elementtype retrieve(position p);
struct treenode{
elementtype element;
searchtree left;
searchtree right;
};
searchtree makeempty(searchtree t){
if(t != null){
makeempty(t->left);
makeempty(t->right);
free(t);
}
return null;
}
position find(elementtype x, searchtree t){
if(t == null)
return null;
else if(x < t->element)
return find(x, t->left);
else if(x > t->element)
return find(x, t->right);
else
return t;
}
position findmin(searchtree t){
if(t == null)
return null;
else if(t->left == null)
return t;
else
return findmin(t->left);
}
position findmax(searchtree t){
if(t != null)
while(t->right != null)
t = t->right;
return t;
}
searchtree insert(elementtype x, searchtree t){
if(t == null){
t = (searchtree)malloc(sizeof(struct treenode));
t->element = x;
t->left = t->right = null;
}
else if(x < t->element)
t->left = insert(x, t->left);
else if(x > t->element)
t->right = insert(x, t->right);
// else x is in the tree already, we'll do nothing!
return t;
}
searchtree delete(elementtype x, searchtree t){
position tmpcell;
if(t == null)
printf("element not found\n");
else if(x < t->element)
t->left = delete(x, t->left);
else if(x > t->element)
t->right = delete(x, t->right);
else if(t->left && t->right){
tmpcell = findmin(t->right);
t->element = tmpcell->element;
t->right = delete(tmpcell->element, t->right);
}
else{
tmpcell = t;
if(!(t->left))
t = t->right;
else if(!(t->right))
t = t->left;
free(tmpcell);
}
return t;
}
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
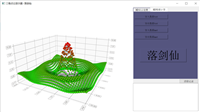
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论