潘嗣敬,洛克王国3366,巧嫁强娶
目录
@(位操作实现简单函数)
给出15个函数,规定了实现每个函数需要的逻辑和算术操作符(规定数量)。
只能使用规定的操作符! ˜ & ˆ | + << >>
不能使用循环或者条件语句
不能使用超过8位的常数(ff)
/*
* pow2plus1 - returns 2^x + 1, where 0 <= x <= 31
*/
int pow2plus1(int x) {
/* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */
return (1 << x) + 1;
}
/*
* pow2plus4 - returns 2^x + 4, where 0 <= x <= 31
*/
int pow2plus4(int x) {
/* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */
int result = (1 << x);
result += 4;
return result;
}
/* bitxor - x^y using only ~ and &
* example: bitxor(4, 5) = 1
* legal ops: ~ &
* max ops: 14
* rating: 1
*/
int bitxor(int x, int y) {
return (~(x&y))&(~(~x&~y));//列出真值表
}
/* tmin - return minimum two's complement integer
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 4
* rating: 1
*/
int tmin(void) {
return 1<<31;//0x80000000
}
/* istmax - returns 1 if x is the maximum, two's complement number,
* and 0 otherwise
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | +
* max ops: 10
* rating: 1
*/
int istmax(int x) {
return !(x+x+2) & !!(~x);//x+1+x+1溢出并且非全一
//x: 0111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
//x+1: 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
//x+1+x: 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
//x+1+x+1:0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
}
/* alloddbits - return 1 if all odd-numbered bits in word set to 1
* where bits are numbered from 0 (least significant) to 31 (most significant)
* examples alloddbits(0xfffffffd) = 0, alloddbits(0xaaaaaaaa) = 1
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 12
* rating: 2
*/
int alloddbits(int x) {
x = (x>>16) & x;
x = (x>>8) & x;
x = (x>>4) & x;
x = (x>>2) & x;
return (x>>1)&1;
// &运算符的“归一性”
//1010 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010 1010
//0000 0000 0000 0000 1010 1010 1010 1010
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010 1010
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010
//0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010
// 可以反推理解:后四位四次翻转得第一行
// 只要倒数第二位为1成立,反推后所有的奇数位都为1
}
/* negate - return -x
* example: negate(1) = -1.
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 5
* rating: 2
*/
int negate(int x) {
return ~x+1; //带符号位取反加一即为相反数
}
/* isasciidigit - return 1 if 0x30 <= x <= 0x39 (ascii codes for characters '0' to '9')
* example: isasciidigit(0x35) = 1.
* isasciidigit(0x3a) = 0.
* isasciidigit(0x05) = 0.
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 15
* rating: 3
*/
int isasciidigit(int x) {
// 0x30 = 0011 0000b 0x39 = 0011 1001b
int a = (x>>4) ^ 0x3; // 判断5、6位是否全1
int b0 = (x>>3) & 1; // 判断第4位是否为1
int b1 = (x>>2) ^ 1; // 判断第3位是否为1
int b2 = (x>>1) ^ 1; // 判断第2位是否为1
return (!a) & ((!b0) | (b0&b1&b2));
// 如果5、6位全1 且 (4位为0或4位为1,2、3位为0)
}
/* conditional - same as x ? y : z
* example: conditional(2,4,5) = 4
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 16
* rating: 3
*/
int conditional(int x, int y, int z) {
x = !x; // 将x设置为0或1
x = (x<<31)>>31; // 将x的0或1拓展到32位全0或全1
return (~x&y) | (x&z); // x为真则~x全1返回y,为假则x全1返回z
}
/* islessorequal - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* example: islessorequal(4,5) = 1.
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 24
* rating: 3
*/
int islessorequal(int x, int y) {
int z,s,sx,sy;
sx = (x>>31)&1; // 取x的符号位
sy = (y>>31)&1; // 取y的符号位
z = x + ~y + 1; // z = x-y
s = ((z>>31) & 1) | (!(z^0));
// 取z的符号位,s为真时x<y或者z全0(x==y)
return ((!(sx^sy))&s) | (sx&(!sy));
// xy同号且z<=0 或 x<=0 y>=0
}
/* logicalneg - implement the ! operator, using all of
* the legal operators except !
* examples: logicalneg(3) = 0, logicalneg(0) = 1
* legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 12
* rating: 4
*/
int logicalneg(int x) {
// |运算符的“分裂性”
x |= x>>16; // 若高16位有1,则传递给低16位的对应位
x |= x>>8; // 若低16位的高8位有1,则传递给低8位的对应位
x |= x>>4; // 若低8位的高4位有1,则传递给低4位的对应位
x |= x>>2; // 若低4位的高2位有1,则传递给低2位的对应位
x |= x>>1; // 若低2位的高1位有1,则传递给最低1位
x ^= 1; // 只要x包含1,则必定会导致此时的x为1,x^=1即取反
return x&1;
}
/* howmanybits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in
* two's complement
* examples: howmanybits(12) = 5
* howmanybits(298) = 10
* howmanybits(-5) = 4
* howmanybits(0) = 1
* howmanybits(-1) = 1
* howmanybits(0x80000000) = 32
* legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* max ops: 90
* rating: 4
*/
int howmanybits(int x) {
int s,c1,c2,c3,c4,c5,c6;
int cnt = 0; // 计数
s = (x>>31)&1; // 符号位
x = ((s<<31)>>31) ^ x; // 取反x
s = !!(x>>16); // 判断高16位是否有1,有则s为1
c1 = s<<4; // 若高16位有1,则低16位可以计数16
x >>= c1; // 右移将已经计数的位移除,c1若为0,则用折半的长度判断
s = !!(x>>8); // 用8位的长度去判断,有效位的个数计入c2
c2 = s<<3;
x >>= c2;
s = !!(x>>4); // 用4位的长度去判断,有效位的个数计入c3
c3 = s<<2;
x >>= c3;
s = !!(x>>2); // 用2位的长度去判断,有效位的个数计入c4
c4 = s<<1;
x >>= c4;
s = !!(x>>1); // 用1位的长度去判断,有效位的个数计入c5
c5 = s;
x >>= c5;
c6 = !!x; // 判断最低位是否为1
cnt = c1+c2+c3+c4+c5+c6+1; // 将每次获得的低位有效位相加,再加1位符号位
return cnt;
}
/* floatscale2 - return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* when argument is nan, return argument
* legal ops: any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* max ops: 30
* rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatscale2(unsigned uf) {
unsigned f = uf;
if ((f & 0x7f800000) == 0)// 如果阶码为0
f = ((f & 0x007fffff) << 1) | (0x80000000 & f);
// 尾数不为0则尾数左移1位,尾数第1位为1则阶码加1,尾数为0则uf为0返回0
else if ((f & 0x7f800000) != 0x7f800000)// 如果阶码不为0,且非全1
f = f + 0x00800000;// 阶码加1
return f;
}
/* floatfloat2int - return bit-level equivalent of expression (int) f
* for floating point argument f.
* argument is passed as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point value.
* anything out of range (including nan and infinity) should return
* 0x80000000u.
* legal ops: any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* max ops: 30
* rating: 4
*/
int floatfloat2int(unsigned uf) {
unsigned inf = 1<<31; // inf = maxint+1
int e = (uf>>23) & 0xff;// 阶码
int s = (uf>>31) & 1; // 符号位
if (uf == 0) return 0;
uf <<= 8; // 左移保留至阶码最后1位
uf |= 1<<31; // 阶码最后一位设为1
uf >>= 8; // 高八位全0
e -= 127; // 阶数
if ((uf & 0x7f80000) == 0x7f80000 || e >= 32)
return inf; // 超过int范围返回inf
if (e < 0) // 小数返回0
return 0;
if (e <= 22) // 位数小于等于22位,尾数位右移
uf >>= 23-e;
else
uf <<= e-23; // 尾数大于22位,尾数为左移
if (s)
uf = ~uf + 1;// 若原uf为负数,则对此处的正数uf取反加1得其相反数
return uf;
}
/* floatpower2 - return bit-level equivalent of the expression 2.0^x
* (2.0 raised to the power x) for any 32-bit integer x.
*
* the unsigned value that is returned should have the identical bit
* representation as the single-precision floating-point number 2.0^x.
* if the result is too small to be represented as a denorm, return
* 0. if too large, return +inf.
*
* legal ops: any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* max ops: 30
* rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatpower2(int x) {
unsigned inf = 0xff << 23; // 阶码全1
int e = 127 + x; // 得到阶码
if (x < 0) // 阶数小于0直接返回0
return 0;
if (e >= 255) // 阶码>=255直接返回inf
return inf;
return e << 23;
// 直接将阶码左移23位,尾数全0,规格化时尾数隐藏有1个1作为底数
}
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
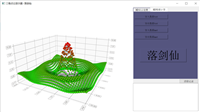
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论