学园默示录,盆栽,秦时明月之焚书坑儒什么时候出
今天在学习拷贝析构的时候遇到的问题:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl;
3 #include "hasptr.h"
4
5 int main()
6 {
7 hasptr ha("halo");
8 cout<<ha.getps()<<endl;
9 hasptr copy_ha(ha);
10 cout<<copy_ha.getps()<<endl;
11 hasptr assign_ha;
12 //hasptr assign_ha = ha;
13 assign_ha = ha;
14 cout<<assign_ha.getps()<<endl;
15 return 0;
16 }
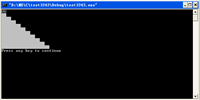
如果按照第12行那样写的话就是初始化过程,这样的话是不会调用重载的拷贝赋值运算符,而是调用拷贝构造函数。如果按照第11和13行这样写,第13行是赋值操作,所以会调用重载的拷贝赋值运算符。以下是运行结果(图1是直接初始化,图二是先定义assign_ha然后赋值。):


下面是类的头文件和实现:
1 //hasptr.h
2 #ifndef hasptr_h
3 #define hasptr_h
4
5 #include <iostream>
6 #include <string>
7
8 class hasptr
9 {
10 public:
11 hasptr(const std::string& s = std::string()) : ps(new std::string(s)), i(0) { }
12 hasptr(const hasptr&);
13 std::string* getps() const { return ps; } //由于原本就不可以对私有成员进行操作,所以不必返回引用
14 int geti() const { return i; }
15 hasptr& operator=(const hasptr&);
16 ~hasptr();
17 private:
18 std::string *ps;
19 int i;
20 };
21
22 #endif // hasptr_h
1 //hasptr.cpp
2 #include "hasptr.h"
3
4 hasptr::hasptr(const hasptr& h)
5 {
6 ps = new std::string(*(h.ps));
7 i = h.i;
8 std::cout<<"call the copyctor."<<std::endl;
9 }
10
11 hasptr::~hasptr()
12 {
13 std::cout<<"call the dtor."<<std::endl;
14 delete ps;
15 }
16
17 hasptr& hasptr::operator= (const hasptr& rhs)
18 {
19 std::cout<<"call the assignment operator."<<std::endl;
20 ps = new std::string(*(rhs.ps));
21 i = rhs.i;
22 return *this;
23 }
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
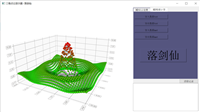
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论