hero s theme,游乐猿,吴雨翔
c++ 内联函数是通常与类一起使用。如果一个函数是内联的,那么在编译时,编译器会把该函数的代码副本放置在每个调用该函数的地方。
对内联函数进行任何修改,都需要重新编译函数的所有客户端,因为编译器需要重新更换一次所有的代码,否则将会继续使用旧的函数。
如果想把一个函数定义为内联函数,则需要在函数名前面放置关键字 inline,在调用函数之前需要对函数进行定义。如果已定义的函数多于一行,编译器会忽略 inline 限定符。
在类定义中的定义的函数都是内联函数,即使没有使用 inline 说明符。
#define _crt_secure_no_warnings
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define max(a, b) \
((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
inline void printab(int a, int b);
int main(void)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
// max(a++, b++);
cout <<"c = " <<c<<endl;
#if 1
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
a++;
b++;
printab(a++, b++);
}
#endif
return 0;
}
inline void printab(int a, int b)
{
cout << "a = " << a << ", b = " << b << endl;
}
默认参数和占位参数在一起 int func(int a, int b, int =0)
#define _crt_secure_no_warnings
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(int a = 666)
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}
//求立方体体积
int get_volume(int len, int width=199, int height=10)
{
cout << "len = " << len << endl;
cout << "w = " << width << endl;
cout << "h = " << height << endl;
return len *width*height;
}
void func2(int x, int=0)//亚元
{
cout << "x =" << x << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
int value = 10;
func();
int len = 10;
int w = 20;
int h = 30;
cout << "体积是" << get_volume(w,h) << endl;
func2(199, 10);
func2(200);
return 0;
}
函数占位参数 运算符重载后置++ int func(int a, int b, int ) 在函数体内部无法使用占位参数
在同一个作用域内,可以声明几个功能类似的同名函数,但是这些同名函数的形式参数(指参数的个数、类型或者顺序)必须不同。您不能仅通过返回类型的不同来重载函数。
#define _crt_secure_no_warnings
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数的返回值, 函数形参列表(参数的个数,参数类型,参数顺序)
//函数重载 函数名相同, 参数列表不同
//函数返回值并不是构成函数重载的条件
int func(int a, int b)
{
cout << "func1" << endl;
return 0;
}
//如果要是函数重载话,不要写默认参数,为了避免调用出现函数冲突
char func(int a, int b, int)
{
cout << "func2" << endl;
return 0;
}
#if 1
int func(int a, char *str)
{
cout << "func3" << endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
void print1(int a)
{
cout << "print 1" << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}
void print1(double b)
{
cout << "print 2" << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}
void print1(char ch)
{
cout << "print 3" << endl;
cout << "ch =" << ch << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
func(10, 20);
func(10, "abc");
print1(10);
print1(19.00);
print1(3.1f);
print1('a');//char->int
//print1("itcast");
//1 如果能够严格匹配调用完全匹配的
//2 如果没有完全匹配,调用隐士转换
//3 都匹配不到,调用失败。
return 0;
}
#define _crt_secure_no_warnings
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int func(int a, int b)
{
cout << "func(int, int)" << endl;
return 0;
}
int func(int a, int b, int c)
{
cout << "func(int, int,int )" << endl;
return 0;
}
//1 . 定义一种函数类型
typedef int(my_func)(int, int);
//2 顶一个指向之中函数类型的指针类型
typedef int(*my_func_p)(int, int);
int main(void)
{
//1.
my_func *fp = null;
fp = func;
fp(10, 20);
//2.
my_func_p fp1 = null;
fp1 = func;
fp1(10, 20);
//3.
int(*fp3)(int, int) = null;
fp3 = func;
fp3(10, 20);
func(10, 20);
func(10, 20, 30);
fp3 = func; //fp3 ---> func(int,int)
//实际上在给函数指针赋值的时候,是会发生函数重载匹配的
//在调用函数指针的时候,所调用的函数就已经固定了。
int(*fp4)(int, int, int) = null;
fp4 = func; //fp4 ---> func(int,int,int)
fp3(10, 30);//func(int,int)
fp3(10, 20);
fp4(10, 30, 30);
return 0;
}
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
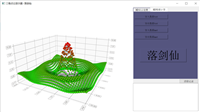
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论