中国竞彩网比分直播,颤抖者极度恐怖网,巨人名录数据

标准流对象
cin ——与标准输入设备相连,istream对象cout ——与标准输出设备相连,ostream对象cerr——与标准错误输出设备相连(无缓冲区,直接屏显)clog——与标准错误输出设备相连(有缓冲区)重定向
freopen("test.txt","w",stdout);
freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
istream类函数
istream& getline(char* str,int maxsize,char delim='\n')从标准输入流中读取maxsize-1个字符,或者遇到默认的换行符\n停止(不包含\n或其他分隔符)int peek()查看输入流首个字符,但不从流中取出istream& putback(char c) 将字符c放置到输入流首部istream& ignore(int num=1,char delim=eof) 从输入流中删掉前num个字符,或遇到分隔符为止输入控制
while(cin>>x){} //istream对象内对强制类型转换符bool进行了重载,具有了判断功能
if(!cin.getline(str,size)){}
十进制dec(默认),oct(八进制),hex(十六进制)
设置宽度 setw(int n)或 cin.width(int n);——设置后是一次性的,可用于cin
设置浮点数精度setprecision(int n)或cout.precision(int n);
fixed或setiosflag(ios::fixed)后则采用定点方式,保留小数点位数(用resetiosflag(ios::fixed)取消对齐方式:left、right
显示正号+:showpos;取消显示正号:noshowpos
补齐字符setfill(char c);
科学计数法:scientific
实现原理
//ostream里对<<进行了重载,函数内部会调用p所指的函数,并以*this为参数,即cout
ostream& operator<< (ostream& (*p)(ostream&));
//用户自定义流操作算子
ostream& tab(ostream& output){
return output<<'\t';
}
需包含头文件<fstream>
因为ifstream和ofstream分别是istream和ostream的派生类,所以也能使用cin和cout的函数
示例
ifstream fin("input.dat",ios::in|ios::binary); //以二进制方式打开文件用于读取数据
ifstream fin; fin.open("input.dat",ios::in|ios::binary); //another way to open file
ofstream fout("c:\\tmp\\output.txt",ios::out|ios::app); //打开字符文件以追加输出数据
if(!fout){
cout<<"file cannot be opened!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
int location=fin.tellg(); //获取读指针的位置(相对于文件开头的字节偏移量)
fin.seekg(location,ios::beg); //将读指针相对文件开头(begin)偏移location个字节
fin.seekg(location,ios::cur); //相对于当前位置(current)偏移
fin.seekg(location,ios::end); //相对于文件尾部(end)偏移
location=fout.tellp(); //写指针当前位置
fout.seekp(location,ios::beg); //seekg为读指针(get),seekp为写指针(print)
fin.close();
fout.close();
文件路径
"c:\\tmp\\output.txt" //绝对路径 //相对路径: "\\tmp\\output.txt" //当前盘符根目录下的tmp文件夹下的文件 "tmp\\output.txt" //当前文件夹下tmp文件夹下的output.txt文件 "..\\..\\tmp\\output.txt" //当前文件夹下的父文件夹的父文件夹下的tmp里的output.txt
二进制文件读写
read(char* str,int size);和write(char *str,int size),将size个字符读取/写入str处(遇文件结尾停止)
gcount()显示read读取的字符数,get(char c)从文件流读取一个字符,put(char c)输出一个字符到文件流
#include<fstream>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct stu{
char name[20];
int score;
}s;
int main(){
ofstream fout("student.dat",ios::out|ios::binary); //open binary file for writing
if(!fout){
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
while(cin>>s.name>>s.score) fout.write((char*) &s,sizeof(s)); //write binary data
fout.close();
ifstream fin("student.dat",ios::in|ios::binary); //open binary file for reading
while(fin.read((char*) &s,sizeof(s))){
cout<<fin.gcount()<<endl;
cout<<s.name<<" "<<s.score<<endl;
}
fin.close();
fstream iofile("student.dat",ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary); //open binary file for i/o
if(!iofile){
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
iofile.seekp(2*sizeof(stu),ios::beg);
iofile.write("mike",strlen("mike")+1); //write ”mike\0" to file
iofile.seekg(0,ios::beg);
while(iofile.read((char*) &s,sizeof(s))) cout<<s.name<<" "<<s.score<<endl;
return 0;
}
因为win\linux\max行末换行格式不同,所以在windows上操作二进制文件时,如果不写ios::binary,windows在读取\r\n时,会自动将\r删除(少了一个字符),写入时自动在\n前加\r(多一个字符)——二进制文件中的\r、\n未必真是用来换行的(unix/linux上加不加ios::binary无所谓)
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
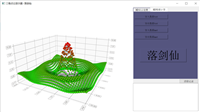
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论