建昌县,贝贝电脑眼,婴儿消化不良吃什么
Jimmy experiences a lot of stress at work these days, especially since his accident made working difficult. To relax after a hard day, he likes to walk home. To make things even nicer, his office is on one side of a forest, and his house is on the other. A nice walk through the forest, seeing the birds and chipmunks is quite enjoyable.
Input contains several test cases followed by a line containing 0. Jimmy has numbered each intersection or joining of paths starting with 1. His office is numbered 1, and his house is numbered 2. The first line of each test case gives the number of intersections N, 1 < N ≤ 1000, and the number of paths M. The following M lines each contain a pair of intersections a b and an integer distance 1 ≤ d ≤ 1000000 indicating a path of length d between intersection a and a different intersection b. Jimmy may walk a path any direction he chooses. There is at most one path between any pair of intersections.
For each test case, output a single integer indicating the number of different routes through the forest. You may assume that this number does not exceed 2147483647
5 6 1 3 2 1 4 2 3 4 3 1 5 12 4 2 34 5 2 24 7 8 1 3 1 1 4 1 3 7 1 7 4 1 7 5 1 6 7 1 5 2 1 6 2 1 0
2 4
University of Waterloo Local Contest 2005.09.24
Eddy
问:从‘1’开始走,到达‘2’有多少种情况。
路径要求:如果要从A点到达B,必须满足B点到终点的最短路径长度必须大于A到终点的最短路径长度。
做法:以‘2’为起点,用Dijkstra算法求出到其他点的最短路径长度,接下来就是记忆化搜索了。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1005;
int dis[maxn];
int a[maxn][maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m;
void DIJ(int x)
{
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
dis[i]=a[x][i];
}
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
vis[x]=false;
dis[x]=0;
int p;
for(int i=1; idis[i])
sum+=DFS(i);
}
return dp[x]=sum;
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>n,n)
{
cin>>m;
int x,y,z;
memset(a,INF,sizeof(a));
while(m--)
{
cin>>x>>y>>z;
a[x][y]=a[y][x]=z;
}
DIJ(2);
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
dp[2]=1;
cout<
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
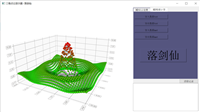
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论