女人公敌第四季,省考时间,河北建材职业技术学院教务处
swift已经推出了一段时间了,今天来总结一下swift与objective-c(以下简称oc)的语法有哪些不同。
1.常量与变量:
在swift中定义常量和变量很简单,常量使用let关键字,变量使用var关键字。
?var numberofrows = 30 let maxnumberofrows = 100
const int count = 10; double price = 23.55; nsstring *mymessage = @"objective-c is not dead yet!";
et count = 10 // count会被识别为int var price = 23.55 // price会被识别为double var mymessage = "swift is the future!" // mymessage会被识别为string
var mymessage : string = "swift is the future!"
在oc中你需要在每一句的后面写上“;”以表达结束,不然会报错,在swift中你不需要再写分号了,当然你写上也没有问题。
var mymessage = "no semicolon is needed"
3.string
在swift中字符串的类型是string,不论你定义的是常量字符串还是变量字符串。
?let dontmodifyme = "you cannot modify this string" var modifyme = "you can modify this string"
在swift中连接两个字符串组成新字符串非常方便,使用“+”:
let firstmessage = "swift is awesome. " let secondmessage= "what do you think?" var message = firstmessage + secondmessage println(message)
在oc中我们使用stringwithformat方法:
nsstring *firstmessage = @"swift is awesome. "; nsstring *secondmessage = @"what do you think?"; nsstring *message = [nsstring stringwithformat:@"%@%@", firstmessage, secondmessage]; nslog(@"%@", message);
?var string1 = "hello" var string2 = "hello"if string1 == string2 { println("both are the same") }
4.array数组
数组的用法swift和oc差不多,我们来看示例:
在oc中:
?nsarray *recipes = @[@"egg benedict", @"mushroom risotto", @"full breakfast", @"hamburger", @"ham and egg sandwich"];
在swift中:?var recipes = ["egg benedict", "mushroom risotto", "full breakfast", "hamburger", "ham and egg sandwich"]
在oc中你可以向nsarray和nsmutablearray中插入任意类型的参数,但是在oc中只能插入相同的参数。和nsarray相似,swift中的array也有很多方法,比如count方法返回数组中的元素个数:
?var recipes : [string] = ["egg benedict", "mushroom risotto", "full breakfast", "hamburger", "ham and egg sandwich"]?var numberofitems = recipes.count // recipes.count will return 5
在oc中你使用nsmutablearray中的方法addobject来增加数组中的元素,swift中的方法更简单,你可以使用“+=”,比如:
recipes += ["thai shrimp cake"]不过请注意这个方法是数组间的,如果一个单个元素要加入数组中请在元素外面增加[]。要取出或者替换数组中的元素,使用索引,这点跟oc中相同:
?var recipeitem = recipes[0] recipes[1] = "cupcake"
在swift中可以使用range来表示范围:比如recipes[1...3] = ["cheese cake", "greek salad", "braised beef cheeks"]这里替换的是recipes中的第二到第四个元素。5.dictionary字典
字典是一种集合类型,由键值对组成,这一点和oc中的nsdictionary很类似,请看示例:
oc中:
?nsdictionary *companies = @{@"aapl" : @"apple inc", @"goog" : @"google inc", @"amzn" : @"amazon.com, inc", @"fb" : @"facebook inc"};
swift中:?var companies = ["aapl" : "apple inc", "goog" : "google inc", "amzn" : "amazon.com, inc", "fb" : "facebook inc"]你也可以声明它的字典类型:?var companies: dictionary = ["aapl" : "apple inc", "goog" : "google inc", "amzn" : "amazon.com, inc", "fb" : "facebook inc"]
要遍历一个字典,需要使用元组来保存每一次循环的字典中的信息:for (stockcode, name) in companies { println("\(stockcode) = \(name)") }
你也可以单独遍历字典中的键或者值:for stockcode in companies.keys { println("stock code = \(stockcode)") } for name in companies.values { println("company name = \(name)") }
如果想给字典添加新的键值对,那么使用如下语句:companies["twtr"] = "twitter inc"
6.class类在oc中创建类的话,会得到两个文件,一个接口文件(.h文件)和一个实现文件(.m文件)。
而在swift中生成类只有一个文件.swift文件。
示例:
class recipe { var name: string = "" var duration: int = 10 var ingredients: [string] = ["egg"] }
在上面的示例中我们创建了一个recipe类,里面有三个属性,并且都声明了类型,做了初始化。在swift中类在初始化的时候它的属性必须都被初始化。如果你不想设置某个属性的默认值的话,使用?把它加入可选链中:class recipe { var name: string? var duration: int = 10 var ingredients: [string]? }这样当你创建一个类的实例的时候:var recipeitem = recipe()
这些可选链中的属性的初始值是nil。你可以给它们赋值:recipeitem.name = "mushroom risotto" recipeitem.duration = 30 recipeitem.ingredients = ["1 tbsp dried porcini mushrooms", "2 tbsp olive oil", "1 onion, chopped", "2 garlic cloves", "350g/12oz arborio rice", "1.2 litres/2 pints hot vegetable stock", "salt and pepper", "25g/1oz butter"]
类可以继承父类和遵守协议,示例:oc中:
?@interface simpletableviewcontroller : uiviewcontroller
swift中:class simpletableviewcontroller : uiviewcontroller, uitableviewdelegate, uitableviewdatasource
7.methods方法swift允许你在类、结构体和枚举中创建方法。
下面是一个没有参数和返回值的方法:
class todomanager { func printwelcomemessage() { println("welcome to my todo list") } }
在oc中调用一个方法的格式如下:todomanager printwelcomemessage];
在swift中调用一个方法的格式如下:todomanager.printwelcomemessage()
如果要建立一个带参数和返回值的方法,格式如下:class todomanager { func printwelcomemessage(name:string) -> int { println("welcome to \(name)'s todo list") return 10 } }
"->"用来指示方法的返回值类型。你可以这样调用上面的方法:
var todomanager = todomanager() let numberoftodoitem = todomanager.printwelcomemessage("simon") println(numberoftodoitem)
8.control flow控制流swift中的控制流和循环颇有c语言的风格。
8.1for循环
for循环使用 for - in的结构,并且可以和range(...或者..<>
for i in 0..
会在控制台输出:
index = 0
index = 1
index = 2
index = 3
index = 4
如果我们使用...这是个闭集合,结果会返回:
index = 0
index = 1
index = 2
index = 3
index = 4
index = 5
如果你想用c中的结构也是可以的:
for var i = 0; i
只不过for后面不用写括号了。
8.2 if-else结构和oc中很像,只不过swift中更简单一些,条件语句不需要写在括号中:
var bookprice = 1000; if bookprice >= 999 { println("hey, the book is expensive") } else { println("okay, i can affort it") }
8.3 switch结构switch中的switch结构拥有非常强大的功能。
示例:
switch recipename { case "egg benedict": println("let's cook!") case "mushroom risotto": println("hmm... let me think about it") case "hamburger": println("love it!") default: } println("anything else")
首先swift中的switch中可以控制字符串,oc中的nsstring是不能被switch控制的,在oc中要实现类似功能你只能使用if-else。另外你可以看到在每个case中我们都没有写break,在oc中你必须在每个case中写break,否则在当前case结束后会进入下一个case,在swift中当前case被执行后就会自动跳出switch,如果需要进入下一个case,添加fallthrough语句。
最后,switch的case中可以包含range操作:
var speed = 50 switch speed { case 0: println("stop") case 0...40: println("slow") case 41...70: println("normal") case 71..
9.tuple元组元组类型在oc中是没有的,它可以包含多种不同的数据类型,你可以把它用作方法的返回值,这样就可以用一个元组来代替返回一个复杂的对象了。例如:
let company = ("aapl", "apple inc", 93.5)
你可以把元组company中的值取出来,用法如下:let (stockcode, companyname, stockprice) = company println("stock code = \(stockcode)") println("company name = \(companyname)") println("stock price = \(stockprice)")
或者company.0、company.1这样的方法也能取到值,更好的做法是在定义元组的时候给每个元素起个名字:let product = (id: "ap234", name: "iphone 6", price: 599) println("id = \(product.id)") println("name = \(product.name)") println("price = usd\(product.price)")
下面是一个把元组作为返回类型的例子:class store { func getproduct(number: int) -> (id: string, name: string, price: int) { var id = "ip435", name = "imac", price = 1399 switch number { case 1: id = "ap234" name = "iphone 6" price = 599 case 2: id = "pe645" name = "ipad air" price = 499 default:break }return (id, name, price) } }
调用:
let store = store() let product = store.getproduct(2) println("id = \(product.id)") println("name = \(product.name)") println("price = usd\(product.price)")
10.optional可选型10.1可选型
可选型通常用在变量之中,可选型的默认值是nil。如果你给一个非可选型的变量赋值nil会报错:
?var message: string = "swift is awesome!" // ok message = nil // compile-time error
当你的类中的属性没有全部初始化的时候会报错:class messenger { var message1: string = "swift is awesome!" // ok var message2: string // compile-time error }
在oc中当你给变量赋值为nil或者没有初始化属性的时候,你是不会收到一个编译时错误的:nsstring *message = @"objective-c will never die!"; message = nil; class messenger { nsstring *message1 = @"objective will never die!"; nsstring *message2;}
但这不代表你不可以在swift使用没有初始化的属性,我们可以使用?来表示这是一个可选型的变量:class messenger { var message1: string = "swift is awesome!" // ok var message2: string? // ok }
10.2那么我们为什么要用可选型呢?swift语言设计的时候有很多安全方面的考虑,可选型表示了swift是一门类型安全的语言,从上面的例子中你可以看到swift中的可选型会在编译时就去检查某些可能发生在运行时的错误。
考虑下面的oc中的方法:
- (nsstring *)findstockcode:(nsstring *)company { if ([company isequaltostring:@"apple"]) { return @"aapl"; } else if ([company isequaltostring:@"google"]) { return @"goog"; } return nil; }
这个方法用来判断输入的字符串是不是apple和google,如果是其他的话返回nil。假设我们在类中定义这个方法,并且在类中使用它:
nsstring *stockcode = [self findstockcode:@"facebook"]; // nil is returned?nsstring *text = @"stock code - "; nsstring *message = [text stringbyappendingstring:stockcode]; // runtime error nslog(@"%@", message);
这段代码是可以通过编译的,但是会在运行时发生错误,原因就是方法中传入facebook返回了nil。
上面oc中的代码我们在swift中的话是这样写的:
func findstockcode(company: string) -> string? { if (company == "apple") { return "aapl" } else if (company == "google") { return "goog" } return nil }var stockcode:string? = findstockcode("facebook") let text = "stock code - " let message = text + stockcode // compile-time error println(message)
这段代码不能通过编译,可以避免运行时的错误了。显而易见,可选型的应用可以提高代码的质量。
10.3解包可选型
在上面我们已经看到了可选型的用法,那么我们如何判断一个可选型的变量有值还是为nil呢?
示例:
var stockcode:string? = findstockcode("facebook") let text = "stock code - " if stockcode != nil { let message = text + stockcode! println(message) }
很像oc中的配对,我们使用if判断语句来做可选型的空值判断。一旦我们知道可选型肯定有值的时候,我们可以使用强制拆封(或者叫解包),也就是在变量名后面加一个感叹号来取得变量的值。如果我们忘记做空值判断会怎样?你进形了强制拆封所以不会发生编译时错误
var stockcode:string? = findstockcode("facebook") let text = "stock code - " let message = text + stockcode! // runtime error
会发生运行时错误,错误提示:
can’t unwrap optional.none
10.4可选绑定
除了强制拆封,可选绑定是一个更简单更好的做法。你使用if - let结构的可选绑定来判断一个变量是不是空值
示例:
var stockcode:string? = findstockcode("facebook") let text = "stock code - " if let tempstockcode = stockcode { let message = text + tempstockcode println(message) }
if let的意思是如果stockcode有值,那么解包它,并且把它赋给一个临时变量tempstockcode,并且执行下面大括号中(条件块)的代码,否则跳过大括号中的代码。因为tempstockcode是一个新的常量,你不必再使用!来获取它的值。
你可以简化这个过程:
let text = "stock code - " if var stockcode = findstockcode("apple") { let message = text + stockcode println(message) }
我们把stockcode的定义放到if中,这里stockcode不是可选型,所以在下面的大括号中也不用再使用!如果它是nil,那么大括号中的代码就不会执行。10.5可选链
我们有一个类code,里面有两个属性code和price,它们的类型是可选型。把上面示例中的stockcode方法的返回值由string改为返回一个code类型。
class stock { var code: string? var price: double? } func findstockcode(company: string) -> stock? { if (company == "apple") { let aapl: stock = stock() aapl.code = "aapl" aapl.price = 90.32 return aapl } else if (company == "google") { let goog: stock = stock() goog.code = "goog" goog.price = 556.36 return goog } return nil }
现在我们计算买了100个苹果需要多少钱:if let stock = findstockcode("apple") { if let shareprice = stock.price { let totalcost = shareprice * 100 println(totalcost) } }
因为findstockcode的返回值是可选值,我们使用可选绑定来判断,但是stock的price属性也是可选的,所以我们又用了一个可选绑定来判断空值。上面的代码运行没有问题,不用if let我们有更简单的办法,你可以把上面的代码改成可选链的操作,这个特性允许我们把多个可选类型用?连接,做法如下:
if let shareprice = findstockcode("apple")?.price { let totalcost = shareprice * 100 println(totalcost) }
如对本文有疑问,请在下面进行留言讨论,广大热心网友会与你互动!! 点击进行留言回复
如何在没有core文件的情况下用dmesg+addr2line定位段错误
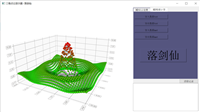
用QT制作3D点云显示器——QtDataVisualization
网友评论